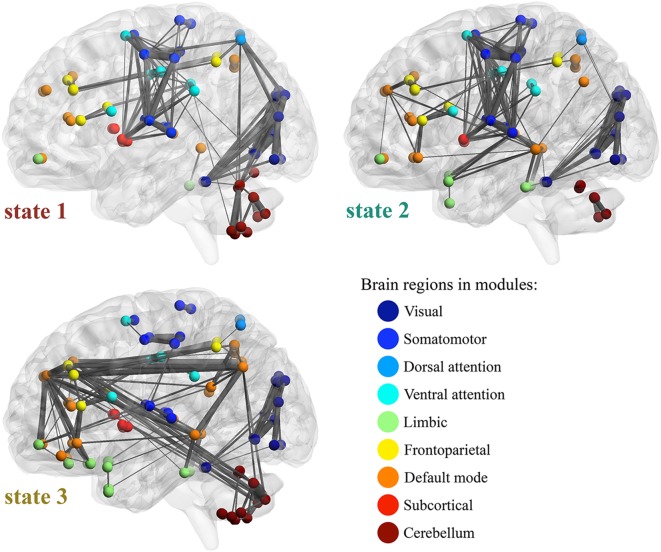
FIGURE 6.
Feature of WFC states. Top 200 functional connections are illustrated in each WFC states, with the Yeo’s 7 functional modules, subcortical and cerebellar regions. The width of the connections represents the connectivity strength. The transition rates among states are indicated by the arrows. For state 1 (WFC-C1), the high FCs in mainly includes functional links both within and across visual, somatomotor, attention and cerebellar (posterior lobe) modules. WFC-C2 was similar with WFC-C1 in those high FCs, however, the FCs in WFC-C2 between cerebellum and the sensory and attention modules were decreased, and higher connections within and across limbic, default mode and frontoparietal modules, in which medial temporal gyrus (MTG), Superior temporal gyrus of temporal pole (TPOsup), inferior temporal gyrus (ITG), inferior parietal gyrus (IPG), dorsolateral superior frontal gyrus (SFG) and medial superior frontal gyrus (SFG medial) are highly involved. In WFC-C3, FCs within sensory and attention modules are still active, but FCs across those modules are decreased. Another feature of WFC-C3 high values of FCs in default network modules, as well as FCs across modules including default, limbic and cerebellum networks. MTG, precuneus (PCUN), angular gyrus (ANG), middle frontal gyrus (MFG), superior parietal gyrus (SPG), and Crus1/Crus2 in cerebellum are highly involved.