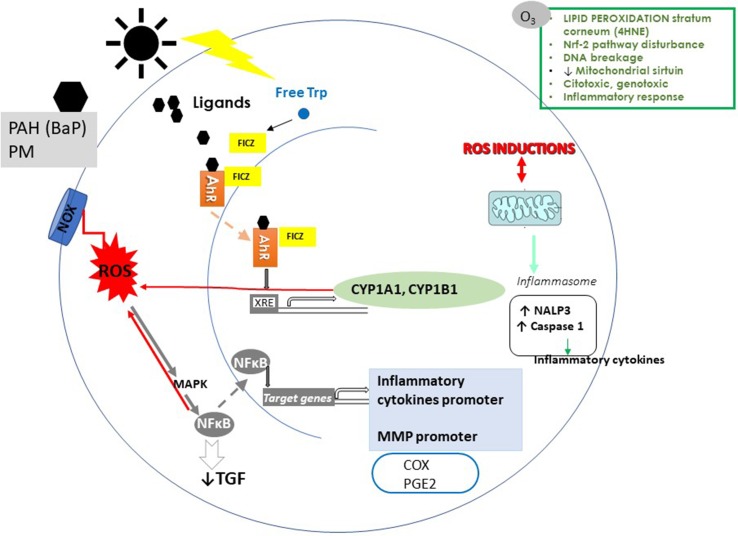
Figure 1.
Effects of air pollution and ultraviolet radiation (UVR) on the skin. A simplified representation of the effects of epidermal keratinocyte effects of particulate matter (PM), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), ozone (O3), and UVR. The AhR binds to PM, PHA, O3, and UVR adducts. After ligand binding, AhR translocates to the nucleus and induces the transcription of cytochrome P450 (CYP 1A1, CYP 1B1). CYP 1A1 generates toxic and reactive intermediates of xenobiotics, increasing ROS. In addition to the canonical AhR pathway, the activation of AhR affects NF-κB pathways. NF-κB induces an increase of proinflammatory cytokines and MMP and decreases TGF-β, and I collagen synthesis. ROS also induces NF-κB activation. Among the next targets of the pollutants are the proinflammatory mediators (COX and PGE2). Pollutants induce the production of NALP3a. NALP3 stimulates caspase-1 to promote proinflammatory cytokines. In epidermal KC, AhR activation results from the absorbance of UVB radiation by tryptophan (Trp). Trp induces the generation of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ). FICZ is a high-affinity ligand for AhR. ROS induced by pollutants alters lipids, proteins, and DNA. Also, oxidative stress causes overexpression of MMP in the ECM and collagen degradation.