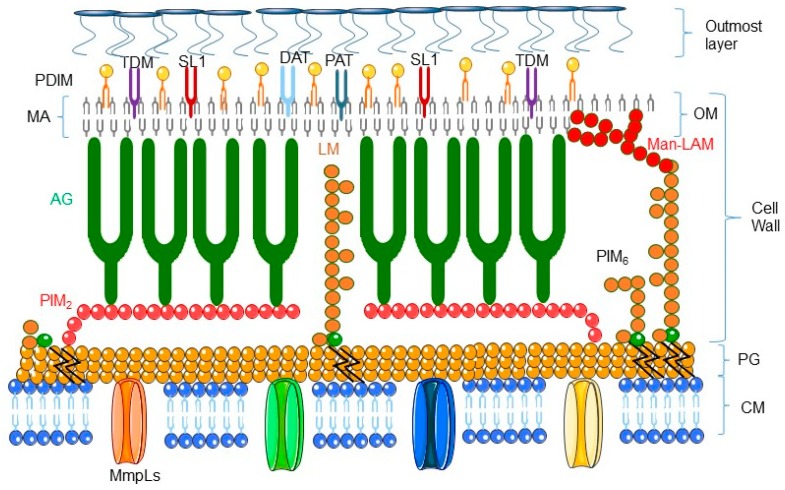
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the cell envelope of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (adapted from [2]). The cell envelope of M. tuberculosis includes an inner cell membrane (CM), a network of peptidoglycan (PG) with covalently attached macromolecules: AG, PIM2, PIM6, LM, and Man-LAM; an outer membrane (OM) composed of mycolic acid (MA), attached to TDM, DAT, PAT, PDIM, and SL-1; and an outmost layer of polysaccharides and proteins. AG: arabinogalactan; DAT: diacyltrehalose; LM: lipomannan; Man-LAM: mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan; PAT: poliacyltrehalose; PDIM: phthiocerol dimycocerosate; PIM2: phospho-myo-inositol-dimannoside; PIM6: phospho-myo-inositol-hexamannoside; MmpL: mycobacterial membrane protein large; TDM: trehalose dimycolate; SL-1: sulphoglycolipid.