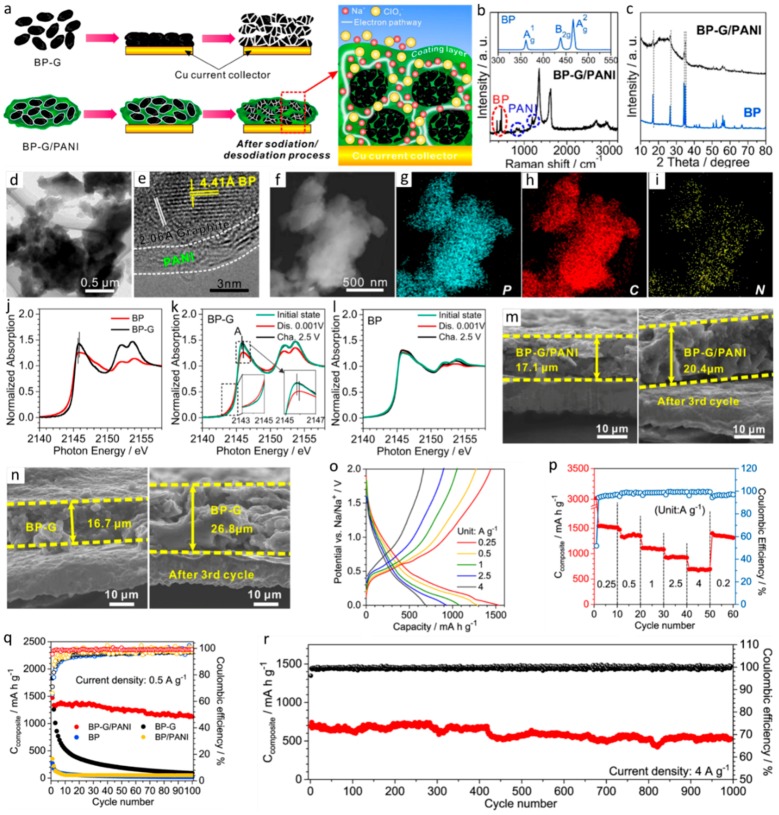
Figure 4.
Structural characterization and electrochemical performance analysis of P-based anode (BP-G/PANI) in SIBs: (a) Schematic representation of sodiation process of black phosphorous-graphite (BP-G) and black phosphorous-graphite with polyaniline (BP-G/PANI). (b) Raman spectra shows the feature peaks of BP, graphite, and PANI. (c) XRD patterns show the characteristic diffraction peaks for BP at 2ϴ values of 16.8, 26.5, 34.1, and 34.9°, a broad peak for PANI at ~22°. Raman spectra and XRD patterns confirm that BP particles remain intact in the BP-G/PANI composite. (d) TEM image and (e) HRTEM image of BP-G/PANI characterize the micro-structure. TEM and HRTEM image confirm that the BP particle are well coated with PANI. (f–i) TEM mappings of BP-G/PANI confirm the uniform distribution of P, C, and N in BP-G/PANI. (j) X-Ray absorption spectra of P state in BP and BP-G shows higher absorption edge in BP-G corresponding to higher charge transfer. (k,l) Ex situ XAS of P K-edge of BP-G and BP indicate the formation NAxP by sodiation in BP-G. (m,n) Cross-sectional SEM images of BP-G/PANI electrode and BP-G electrode show that PANI coatings attenuate the volume changes in electrode, providing a long cycling ability for BP-G/PANI. (o) The voltage profiles of BP-G/PANI at different current densities in the potential range: (0.01–2.00 V). The capacity loss in the first cycle is attributed to the SEI film formation. (p) Rate capability test of BP-G/PANI anode shows that it can deliver 690 mAh g−1 (45% capacity retention) at high current rate of 4 A g−1. (q) The cycling stability and coulombic efficiency of BP, BP-G, BP-G/PANI at 0.5 A g−1 show that the reversible capacity of BP-G/PANI is mostly contributed by BP. (r) The cycling ability and coulombic efficiency of BP-G/PANI anode at 4 A g−1 show that it can deliver a reversible capacity 520 mAh g−1 after 1000 cycles. Reprinted with permission from [92]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society.