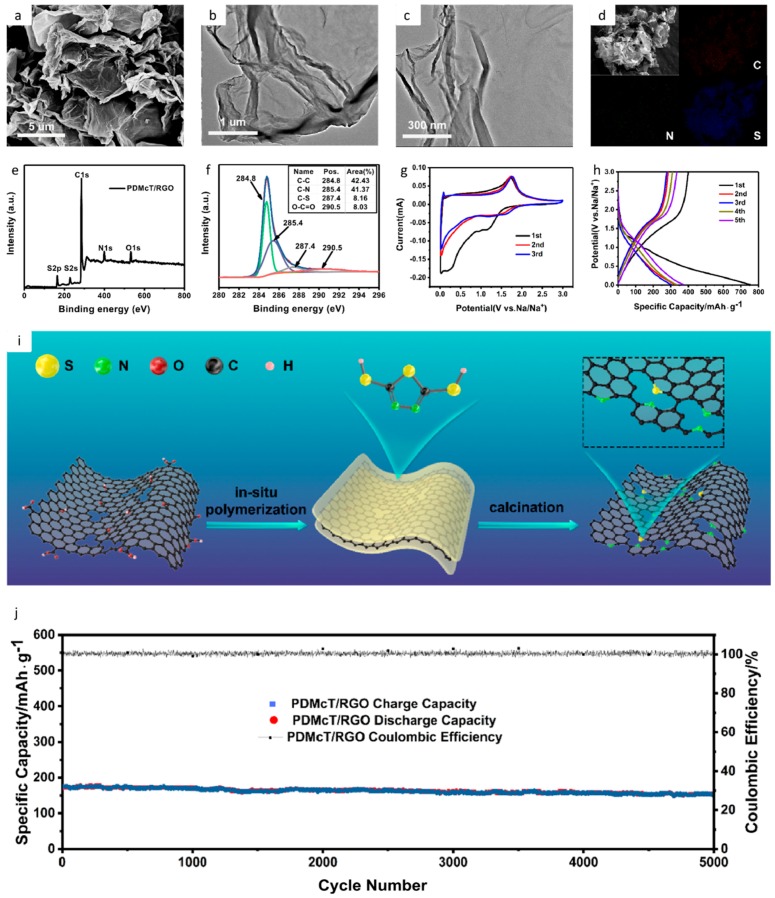
Figure 7.
Characterization and electrochemical performance analysis of poly(2,5-dimercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole)(PDMcT)/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) (PDMcT/RGO) as an anode in SIBs: (a) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of the material, (b,c) transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of the material, (d) energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) elemental mapping of the material indicating the homogeneous distribution of atoms N, and S co-doping the graphene sheets, (e) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) survey of the material corroborating the results obtained at EDX, (f) high resolution XPS of C 1s showing the C-C, C-N, and C-S characteristic binding energies, (g) cyclic voltammetry curves from 1st to 3rd cycles for voltage range from 0.01–3.0 V at scan rate of 0.1 mV s−1. In the 1st cycle, at approximately 0.2 V, the reduction peak may be assigned to the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation; additionally, at approximately 0 and 0.09 V, redox peaks may be assigned, respectively, to Na+ insertion/extraction from graphene layers, (h) charge and discharge curves at current density of 50 mA g−1, (i) representation of the synthesis of the material PDMcT/RGO, and (j) specific capacity representation versus cycle number for current density of 5000 mA g−1 showing the low drop in capacity even after 5000 cycles; thus, remaining at 153.3 mAh g−1. Reprinted with permission from [155]. Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.