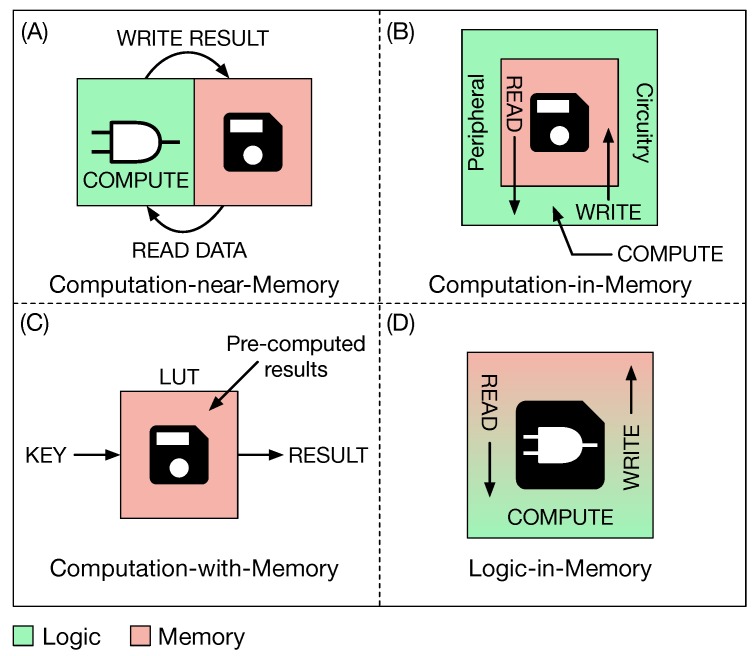
Figure 1.
Depending on how the memory is used for computing data, four main in-memory computing approaches can be defined. (A) Computation-near-Memory (CnM): 3D-integration technologies allow one to bring computation and storage closer together by reducing the length of the interconnections. Logic and storage are still two separate entities. (B) Computation-in-Memory (CiM): The standard memory structure is not modified, while data computation is performed in the peripheral circuitry. (C) Computation-with-Memory (CwM): Memory is used as a Look Up Table to retrieve pre-computed results. (D) Logic-in-Memory (LiM): Data computation is performed directly inside the memory by adding simple logic in each memory cell.