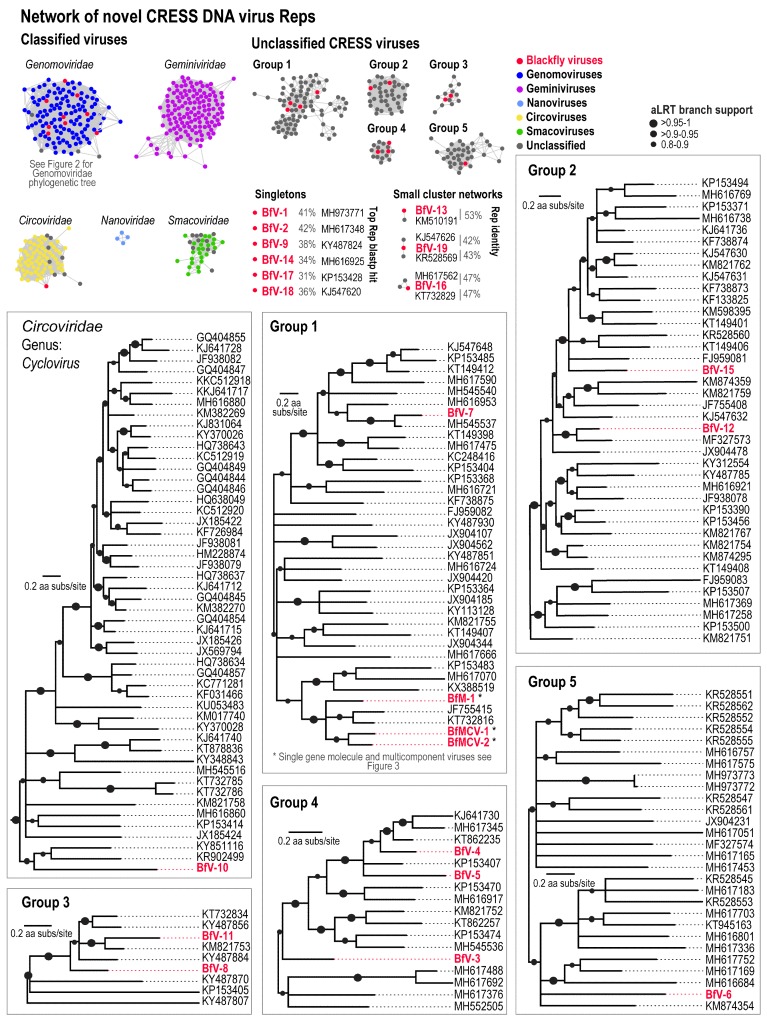
Figure 1.
A network and phylogenetic analyses of the circular replication-associated (Rep) protein encoding single-stranded (CRESS) DNA virus replication-associated (Rep) protein sequences. The network analyses shows the clustering of the blackfly CRESS DNA viruses (shown as red circles) within taxonomic family groupings, larger and smaller groupings of unclassified CRESS DNA viruses (only those groups containing CRESS DNA viruses from this study), and singletons from this study that do not cluster with other known Reps. Closest Rep comparisons and percentage similarity are shown for the smaller groups and singletons. Maximum likelihood phylogenetic trees of the Rep sequence of circovirus (showing only the Cyclovirus genus clade) and the five larger unclassified CRESS DNA virus groupings. Blackfly originating sequence names are shown in red. The maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of the Rep sequence for the genomoviruses is shown in Figure 2.