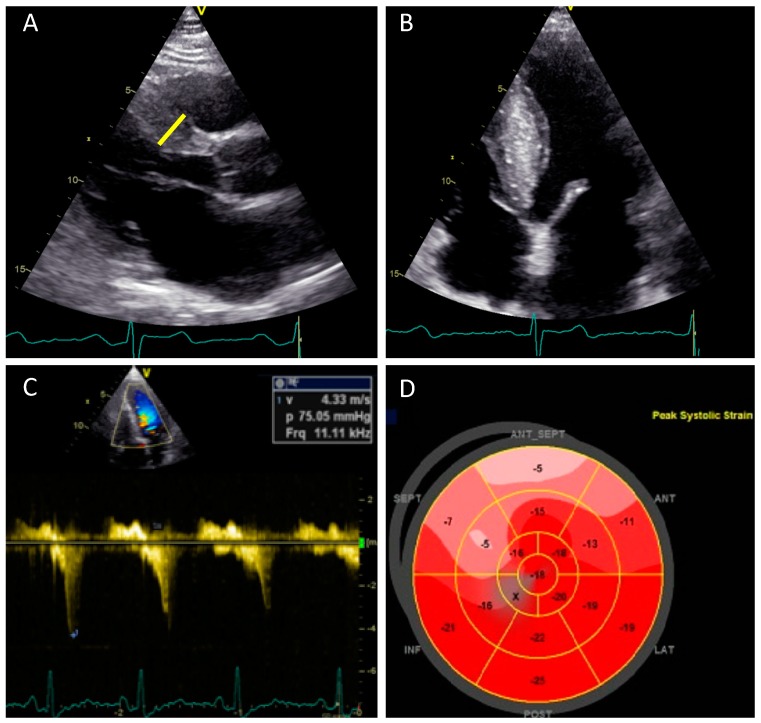
Figure 2.
The role of transthoracic, two-dimensional echocardiography in the assessment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). (A) A parasternal long axis view showing basal septal hypertrophy (maximum LV wall thickness 21 mm—yellow line). (B) Apical four-chamber view shows hypertrophy of the interventricular septum. (C) Continuous wave Doppler from modified apical five-chamber view showing a rest dynamic gradient of 75 mmHg in the LVOT (D) A bull’s eye plot of two-dimensional speckle tracking showing reduced peak longitudinal strain values in the septum—the areas most affected by hypertrophy with preservation of the basal-to-apical gradient. HCM—hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, LV—left ventricle, and LVOT—left ventricular outflow obstruction.