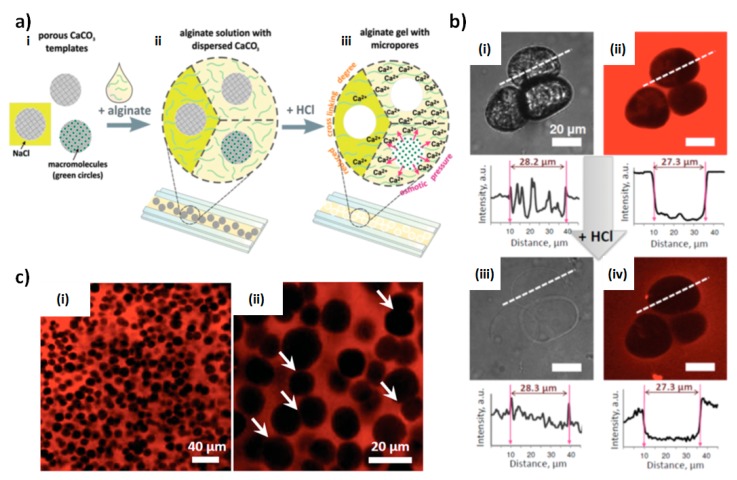
Figure 5.
(a) Schematics of formation of porous alginate hydrogels. (i,ii) Dispersion of CaCO3 crystals in alginate solution followed by deposition of the suspension onto a glass substrate. (ii,iii) Formation of porous hydrogel by addition of HCl, which induces CaCO3 dissolution. The dissolution process is accompanied by alginate cross-linking and formation of hollow pores. (b) Optical transmission and fluorescent images of 33 μm vaterite CaCO3 crystals dispersed in alginate before (i,ii) and after (iii,iv) addition of HCl. Fluorescence profiles are given to each image and taken along the white interrupted lines. (c) CSLM images of porous alginate gel formed at compact packing of 11 μm CaCO3 templates. White arrows in (c,ii) indicate interconnected pores. The gel (b,c) has been stained with rhodamine 6G. Reproduced with permission from [18], published by John Wiley & Sons, 2015.