Figure 5.
The Cap and Plug Modules Are Required to Control Intercellular Communication upon Ionophore Treatment
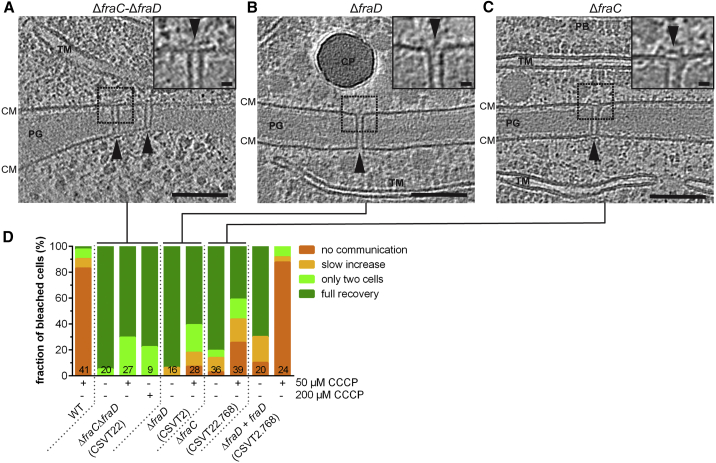
(A–C) SJs from the ΔfraC-ΔfraD (A) and ΔfraD (B) mutants were missing the cap and plug modules. SJs from ΔfraC (C) showed a mixture of fully assembled and misassembled SJs (insets show magnified views; bars, 10 nm). Shown are 13.5 nm-thick sections through cryotomograms; bars, 100 nm. CM, cytoplasmic membrane; CP, cyanophycin; PB, phycobilisomes; PG, septal peptidoglycan; TM, thylakoid membranes.
(D) FRAP experiments of the wild type and the mutants shown in (A)–(C). The CCCP-treated ΔfraD and ΔfraC single mutants showed a much smaller fraction of non-communicating cells than in the CCCP-treated wild type, indicating that the mutants were unable to gate communication. Strain CSVT2.768 is a complementation of the ΔfraD mutant and showed wild type behavior. “+” and “−” indicate the presence and absence of CCCP. Numbers within the bars indicate the number of analyzed cells (n) from different filaments. Results from at least two independent cultures were cumulated (except for ΔfraC-ΔfraD treated with 200 μM CCCP).
See also Figure S5.