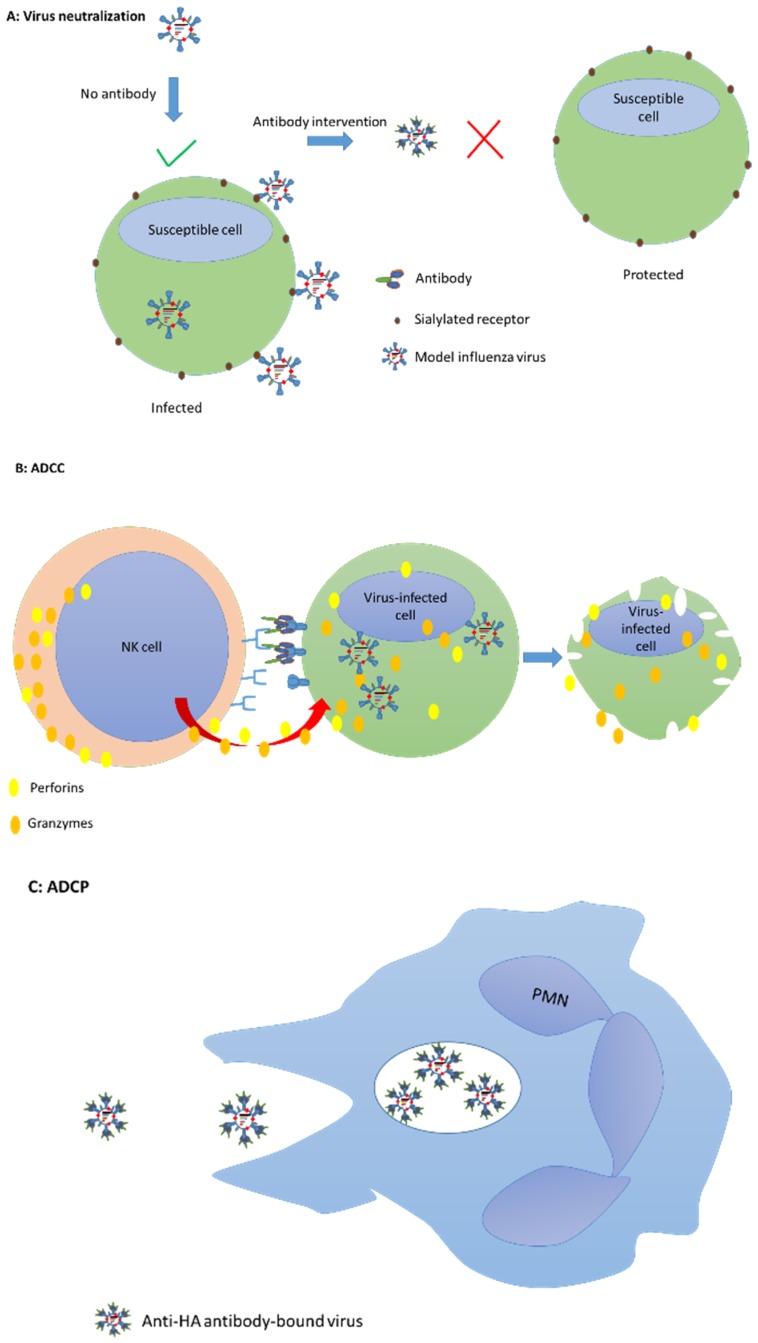
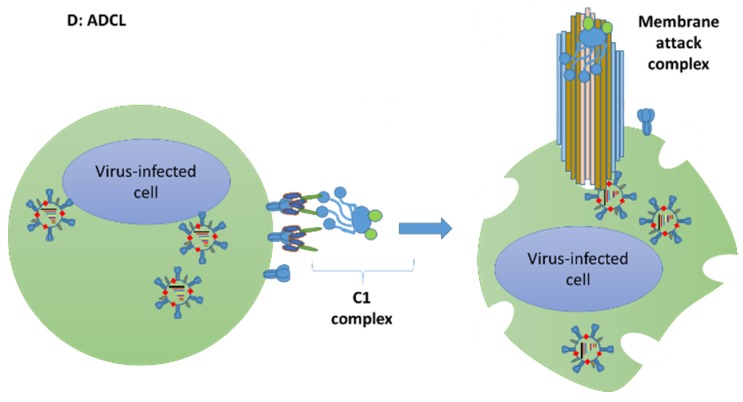
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of antibody protection via passive immunization. This figure outlines the possible mechanisms by which antibodies could mediate instant protection when administered either as a prophylaxis or treatment. (A) Broadly neutralizing antibodies interact with HA interfering with the virus attachment to host cell. (B) Opsonized infected host cells attract natural killer (NK) cell destruction via the process of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). (C) Opsonized virus particles activate their phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear cells (PMN) via the process of antibody-mediated cell phagocytosis. (D) Virus infected cells displaying the surface proteins of replicating viruses attract the assembly of the classical complement proteins forming a membrane attack complex that destroys the cell by osmosis in a process called antibody-dependent cell lysis (ADCL).