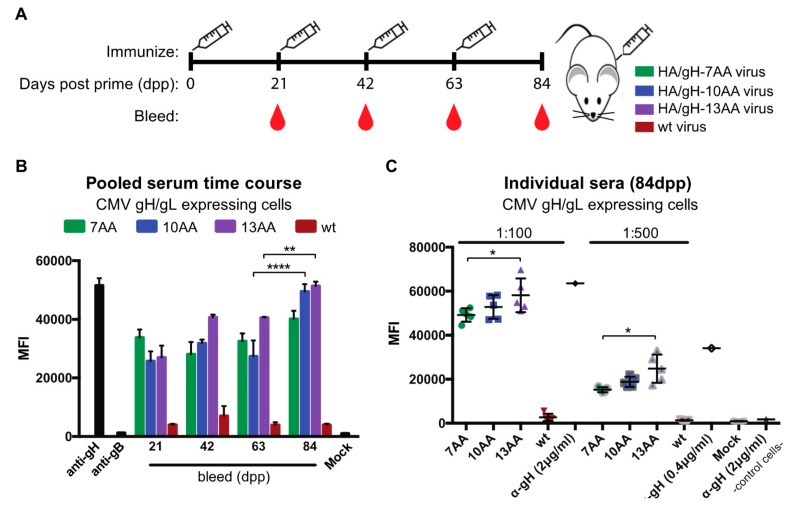
Figure 4.
Chimeric influenza/CMV viruses generate a humoral response against CMV gH. (A) The immunization (syringe) and blood collection strategy for groups of five mice immunized with either chimera HA/gH viruses HA/gH-7AA (7AA), HA/gH-10AA (10AA), and HA/gH-13AA (13AA) or the wild type IAV virus (wt) lacking CMV components is depicted. Blood collection occurred prior to immunization. (B) Pooled sera from each immunization group was analyzed for specificity to cells expressing the CMV gH/gL dimer by measuring immunoglobulin binding followed by anti-mouse Ig-conjugated to Alexa647 (αmouse-IgAlexa647) with flow cytometry. Controls included anti-gH (10C10) and anti-gB (2F4) (2 and 0.4 µg/mL) mAbs as well as cells probed with only αmouse-IgAlexa647 (Mock). (C) Serum from individual mice at 84 days post prime (dpp) was subjected to flow cytometry analysis of CMV gH/gL-expressing cells. Anti-CMV gH mAb were utilized as a positive and negative control, respectively. Mock represents cells probed with αmouse-IgAlexa647only and control cells refer to non-gH/gL expressing cells. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was determined using FlowJo Software and the data points were from technical replicates with s.d. depicted. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 (ANOVA).