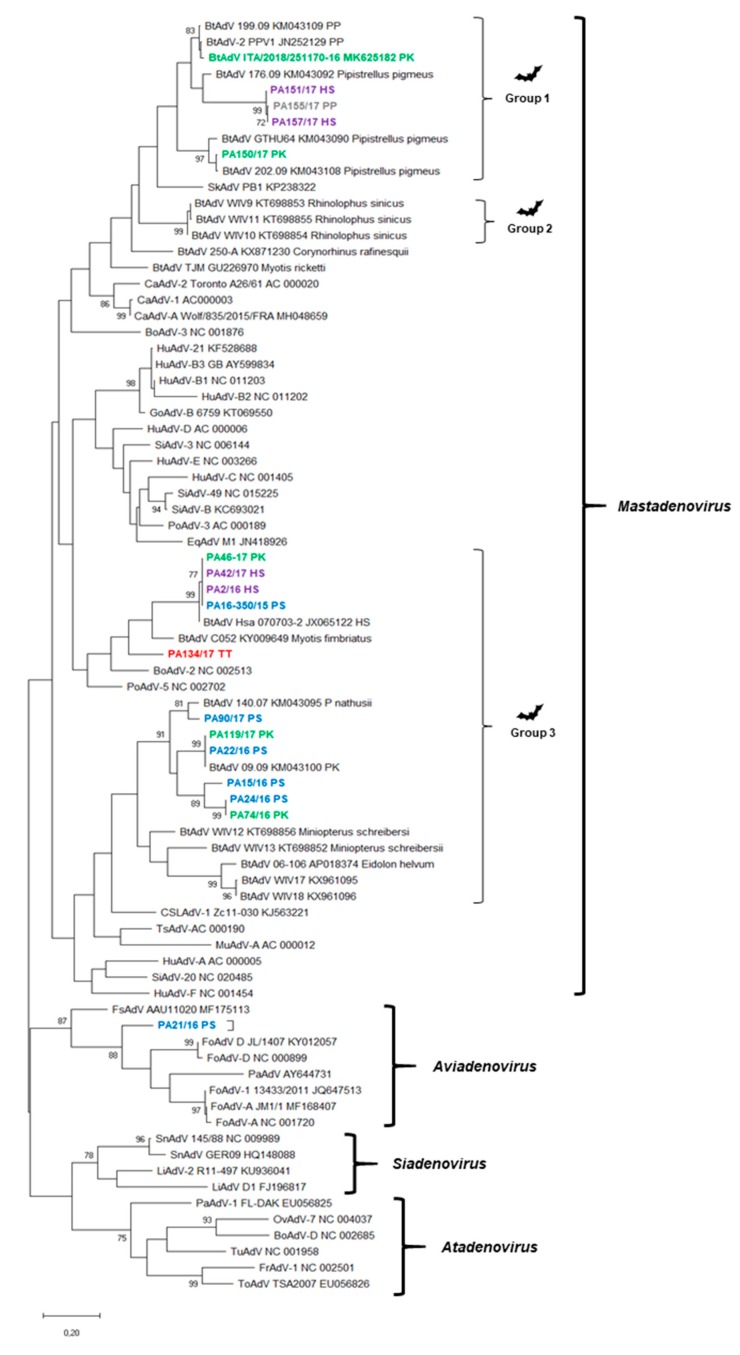
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic tree based on the partial polymerase-coding region (233 nt positions) of adenoviruses. GenBank accession numbers are provided for reference strains. The tree was generated using the maximum-likelihood method with the Jukes–Cantor method by bootstrapping over 1000 replicates. Bootstrap values >70% are shown. Scale bar indicates nt substitutions per site. Blackarrows indicates the strains sequenced in this study. PS, Pipistrellus spp. (blue color); PP, Pipistrellus pipistrellus (grey color); PK, Pipistrellus kuhlii (green color); HS, Hypsugo savii (purple color); TT, Tadarida teniotis (red color). BtAdV, bat adenovirus, SkAdV, skunk adenovirus, EqAdV, equine adenovirus, CaAdV, canine adenovirus, HuAdV, human adenovirus, GoAdV, gorilla adenovirus, SiAdV, simian adenovirus, PoAdV, porcine adenovirus, MuAdV, murine adenovirus, TsAdV, tree shrew adenovirus, CSLAdV, California sea lion adenovirus, BoAdV, bovine adenovirus, FsAdV, fur seal adenovirus, PaAdV, parrot adenovirus, FoAdV, fowl adenovirus, SnAdV, snake adenovirus, LiAdV, lizard adenovirus, OvAdV, ovine adenovirus, TuAdV, turkey adenovirus, ToAdV, tortoise adenovirus, FrAdV, frog adenovirus.