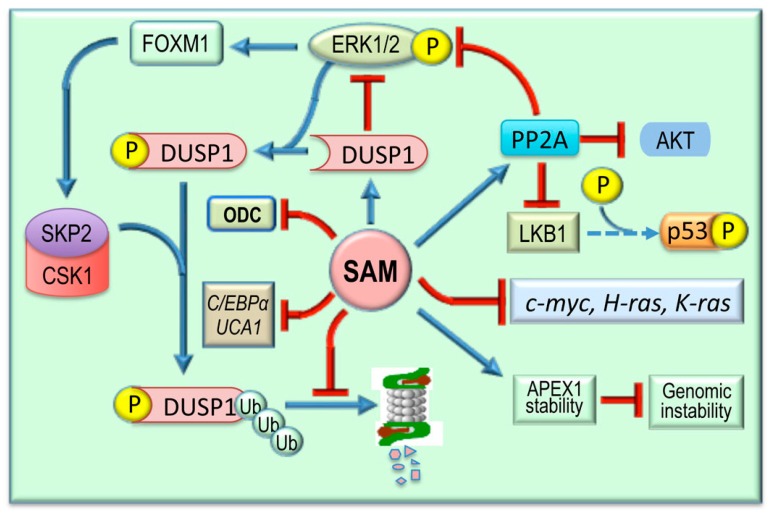
Figure 5.
Effects of SAM on signal transduction pathways. SAM is involved in the stabilization of the DNA repair enzyme APEX1, thus reducing genomic instability. Through the inhibition of LKB1/AMPK axis, SAM controls p53 phosphorylation and cell growth and survival by inducing PPA2 expression that phosphorylates and inactivates AKT and its targets. Moreover, PPA2 activation and DUSP1 stabilization inhibit the RAS/ERK pathway. The inhibition of ERK1/2 activity by DUSP1 is controlled by DUSP1 phosphorylation of Ser296, which allows its ubiquitination by the SKP2–CSK1 ubiquitin ligase and proteasomal degradation, as well as by SKP2–CSK1 activation operated by FOXM1, a major target of ERK1/2. SAM also affects the cell cycle by inhibiting c-MYC, H-ras, and K-ras expression and ODC activity. Finally, the antitumor effects of SAM could also be exerted through inhibition of C/EBPα and UCA1 expression.