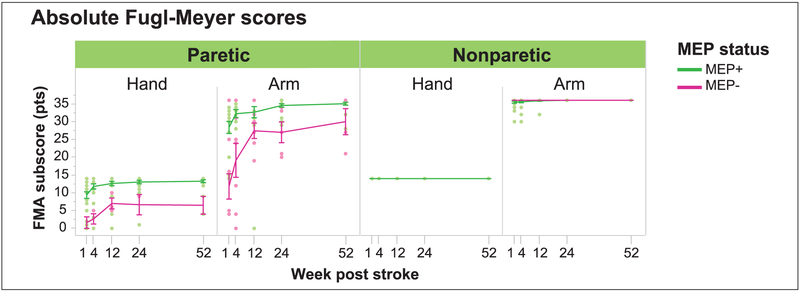
Figure 4.
Effect of MEP status on absolute FMA scores over time in the paretic hand and arm. MEPs were assessed in the FDI and BIC. Absolute FMA subscores are shown for the nonparetic sides for clinical reference. Single-subject data and average values with SEM are shown for each time point. Both paretic hand and arm had reduced FMA scores following stroke, but having an MEP was associated with significantly higher FMA subscores than having no MEP, for both the hand (P < .0001) and arm (P < .0001). FMA recovery curves ran in parallel for paretic hands with and without MEPs. FMA recovery was steeper in arms without MEPs than with MEPs (P = .007). However, hand and arm recovery curves behaved in a largely similar fashion in the absence of MEPs, arriving at a recovery plateau at 12 weeks and not converging on their counterparts with MEPs. MEP, motor evoked potential; FMA, Fugl-Meyer Assessment; FDI, first dorsal interosseous; BIC, biceps; SEM, standard error of the mean.