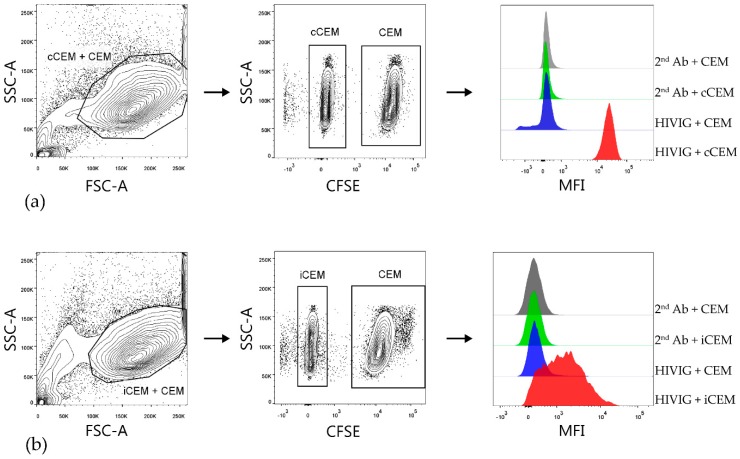
Figure 2.
Gating strategy used to detect HIVIG binding to cCEM and iCEM cells. Both cCEM and CFSE+ CEM (left panel of (a)) or iCEM and CFSE+ CEM cells (left panel of (b)) were gated on. From these, cCEM and iCEM were distinguished from CFSE+ CEM cells (middle panels of (a) and (b) respectively). Binding of secondary antibody specific for human IgG Fc to CEM and cCEM (1st and 2nd rows of right panel of (a)) or CEM and iCEM (1st and 2nd rows of right panels of (b)). Binding of HIVIG primary antibody at 150 μg/mL to CEM and cCEM (3rd and 4th rows of right panel of (a)) and CEM and iCEM (3rd and 4th rows of right panel of (b)) was detected by using a fluorochrome conjugated secondary Ab. FCS-A = forward scatter-area; SSC-A = side scatter-area; CFSE = carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; CEM = CEM.NKr.CCR5; cCEM = recombinant gp120 coated CEM cells; iCEM = HIV infected CEM cells; MFI = mean fluorescence intensity. 2nd Ab = anti-human immunoglobulin G Fc specific secondary antibody; Fc = the fragment crystallizable portion of immunoglobulin G.