Fig. 5. ASPP2-Merlin binding.
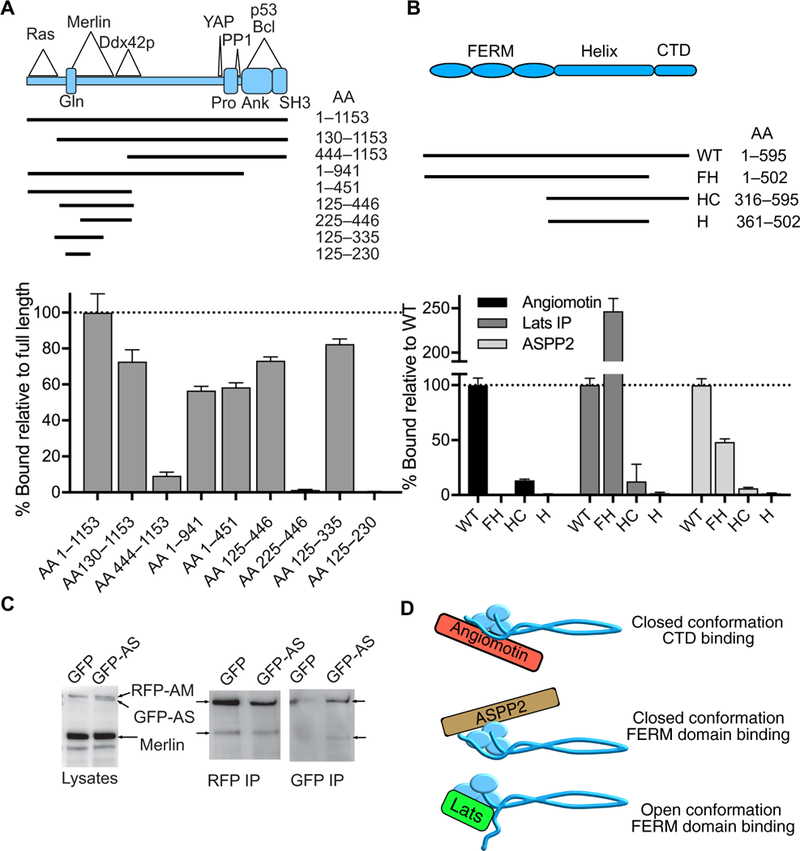
(A) Schematic diagram of ASPP2 deletion mutants used to map the Merlin-binding domain. The regions of known interactions with Ras, Merlin, Ddx42p, YAP, PP1, p53, and Bcl and the known structural domains are noted in the diagram. Gln, Gln-rich domain; Pro, proline-rich domain; Ank, ankyrin repeat region; SH3, SH3 domain; AA, amino acid. Quantification of Merlin-NLuc binding to RFP-ASPP2 deletion mutants using purified proteins. Data are means relative to full-length ASPP2 ± SD; n = 3 biological replicates. (B) Schematic diagram of the domain structure of Merlin and the Merlin-NLuc deletion mutants used to map ASPP2-binding regions. WT, full-length wild-type; FH, FERM-helix (CTD deleted); HC, helix-CTD (FERM deleted); H, helix (CTD and FERM deleted). Quantification of Merlin-NLuc deletion mutants binding to RFP-Angiomotin, RFP-Lats1, and RFP-ASPP2 using purified proteins; n = 3 biological replicates. (C) Lysates of HEK 293T cells cotransfected with Merlin-NLuc and RFP-angiomotin (RFP-AM) and either GFP alone or GFP-ASPP2 (GFP-AS) were subjected to Western blotting, RFP immunoprecipitation (RFP IP), or GFP immunoprecipitation (GFP IP) and probed with a combination of antibodies directed against Merlin, GFP, and RFP. (D) Schematic diagram depicting the proposed protein-protein interactions of different Merlin conformations. We propose that Angiomotin binds to the closed conformation of Merlin at the CTD, ASPP2 binds to the closed conformation of Merlin through the FERM domain, and Lats1 binds to the open conformation of Merlin through the FERM domain.
