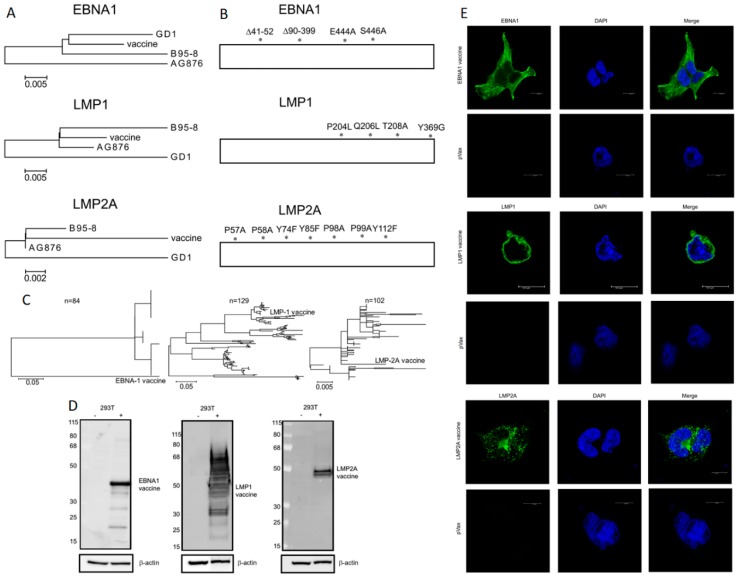
Figure 1.
Design and expression of EBNA1vax, LMP1vax, and LMP2Avax vaccine antigens. (A) Diagram showing the similarity of the consensus sequence of the EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2A vaccines, generated from the sequences of EBV strains B95-8, AG876, and GD1. The vaccine antigen designs use a SynCon sequence embedded in a pVAX plasmid. (B) Modifications were made to the consensus vaccine antigens to avoid potentially oncogenic properties and repetitive sequences. (C) Phylogenic trees showing relationship of vaccines to known EBV latent protein sequences. (D) Western blots showing the expression of vaccine antigens in untransfected cells (left columns) and cells transfected with the DNA vaccine (right columns). Beta-actin was used as a loading control. (E) Immunofluorescence images showing expression of the vaccine antigens in 293T cells, with cytoplasmic EBNA1vax, LMP1vax on the outer membrane, and LMP2Avax showing a vesicular localization. Antigens are labeled in green, and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) shows the nucleus in blue. Scale bars are 10 μm.