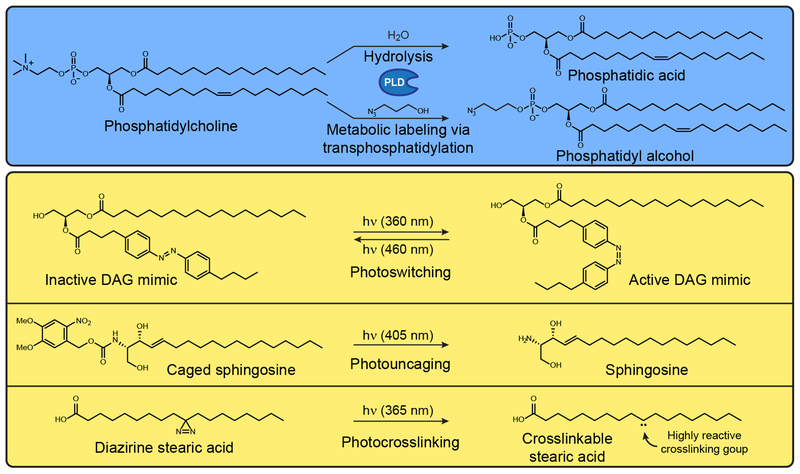
Figure 1. Biochemical and Photochemical Reactions Used in Conjunction with Lipid Probes.
(A) Metabolic labeling of phospholipase D (PLD) activity. PLD functions naturally as a hydrolase that produces phosphatidic acid from phosphatidylcholine, but the addition of low concentrations of exogenous primary alcohols, such as 3-azido-1-propanol, causes PLDs to catalyze a transphosphatidylation reaction to form a functionalized phosphatidyl alcohol. (B) Photochemical reactions that can be used to turn on inactive precursors, including those that can activate photoswitchable (i), photocaged (ii), and photocrosslinkable (iii) lipids. Abbreviation: DAG, diaglycerol.