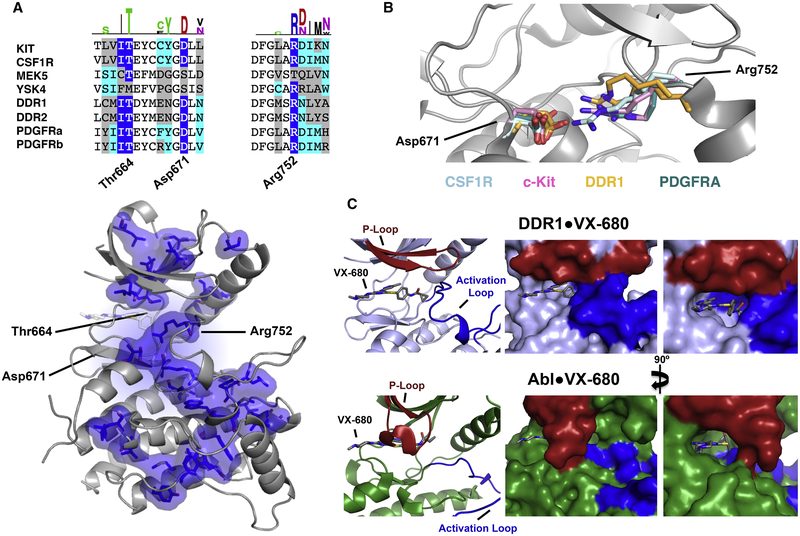
Figure 4: Structural hallmarks of DDR1 and other promiscuous kinases.
A) Sequence alignment of the eight promiscuous kinases around Thr664 (the ‘gatekeeper’ mutant), Asp671, and Arg752 (DDR1 numbering). Dark blue highlights residues enriched in the promiscuous set by 50% or more and cyan indicates residues enriched by 10–50% according to Two Sequence Logo comparison (using p-value cutoff 0.01) of the promiscuous kinases to the other 483 kinases analyzed. Bottom: All residues enriched in our promiscuous set by 50% or more are shown as blue surface on the DDR1-VX680 structure. B) Potential salt bridges between residues equivalent to DDR1 Asp671 and Arg752 are shown for representative structures: CSF1R (PDB IDs: 3KRL and 2IOV) in pale cyan, c-Kit (PDB IDs: IT45 and IT46) in pink, DDR1 (PDB IDs: 5FDP and 5BVO) in orange, and PDGFRA (PDB ID: 5GRN) in teal. C) The structures of VX-680 bound to DDR1 (top) and Abl (bottom, PDB entry 2F4J) illustrate the hydrophobic shield formed by the activation loop (blue) and the P-loop (red), respectively. See also Figure S5.