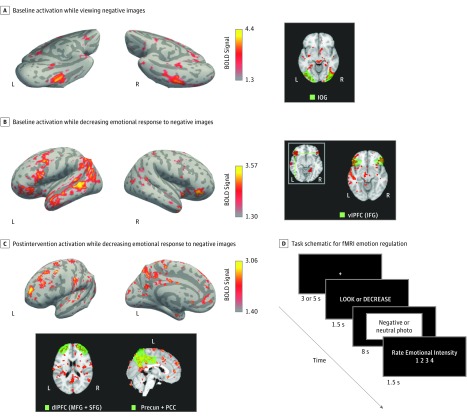
Figure 3. Functional Brain Scan Activation During Emotional Regulation Task.
A, Patterns of activation unique to viewing negative images in the intervention and control groups at baseline. Right panel shows activation of inferior occipital gyrus (IOG), which is associated with the processing of emotionally salient images. B, Patterns of activation unique to the action of decreasing emotional response to negative images (ie, reappraisal) in the intervention and control groups at baseline. Right panel shows activation of ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC), which includes the inferior frontal gyrus (IFG) and is associated with the reinterpretation of affective stimuli to alter the emotional impact. C, Patterns of activation unique to the action of decreasing emotional response to negative images, only seen in the intervention group and only seen after the intervention. Lower panel shows activation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC), which includes the middle frontal gyrus (MFG) and superior frontal gyrus (SFG) and is associated with the functioning of the executive control hub of higher-order cognition. The precuneus (precun), which is anatomically within the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC), is associated with mental imagery, visuospatial motor skills, and self-awareness. Both areas showed activation in the modified mindfulness-based stress reduction arm postintervention. D, Schematic diagram of the timing and steps involved in the presentation of each image for the emotional regulation task. BOLD indicates blood oxygen level–dependent; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; L, left; and R, right.