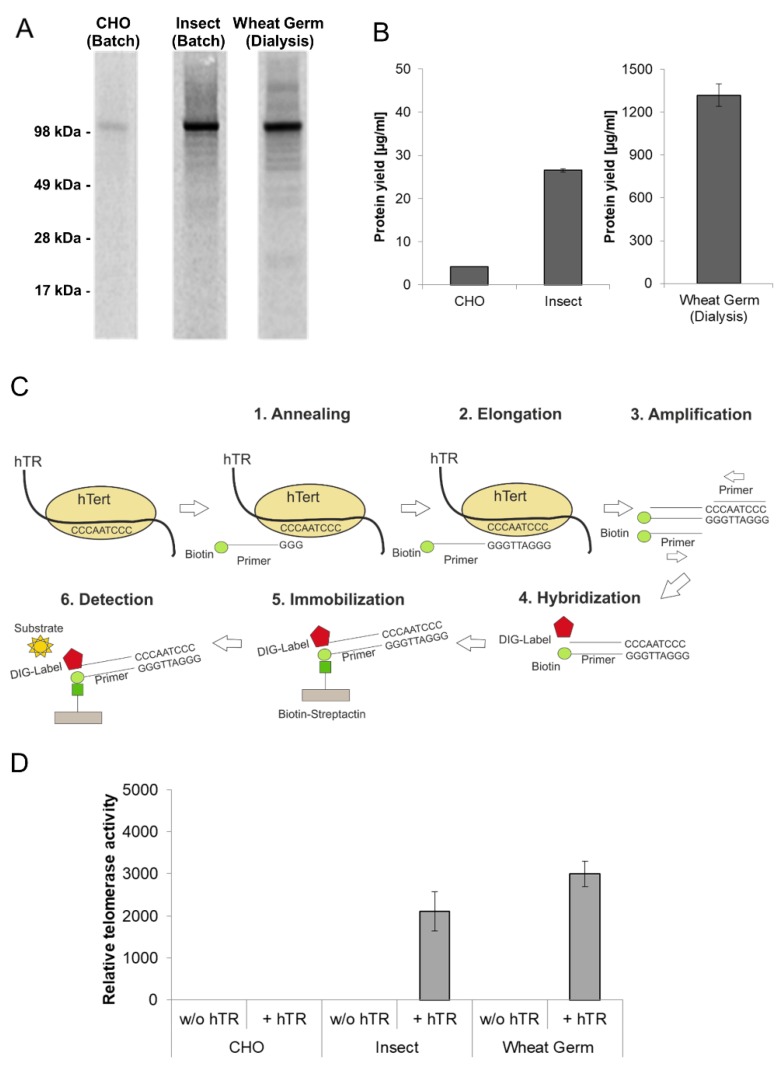
Figure 4.
Quantitative and qualitative characterization of cell-free synthesized human telomerase (hTERT). Synthesis of hTERT in eukaryotic cell-free systems in batch (CHO and Sf21) and dialysis (wheat germ) mode. Protein was labeled with 14C-leucine for further analysis. (A) A 5 µL aliquot of translation reaction mixture was precipitated with acetone and the resulting protein pellets were resolved in sample buffer. Samples were electrophoretically separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel followed by autoradiography. (B) Determination of hTERT protein yield by scintillation measurement. 5 µL of translation mixture was precipitated using TCA and precipitated protein was soaked on a filter sheet. The filter sheet was dissolved in scintillation liquid and analyzed using an LS6500 multi-purpose scintillation counter (PerkinElmer). (C) The general principle of hTERT activity assay (TeloTAGGG Telomerase PCR ELISA PLUS Kit (Roche)). (D) Functional characterization of cell-free synthesized hTERT using TeloTAGGG Telomerase PCR ELISAPLUS Kit. Synthesis of hTERT was carried out in the absence and presence of telomerase-specific RNA (hTR). According to the manufacturer’s protocol (TeloTAGGG Telomerase PCR ELISA PLUS, Roche), samples are considered as telomerase-positive if the difference between the sample and the negative control is higher than the twofold value of the negative control. Samples, where the difference is lower than the twofold value of the negative control, were considered as telomerase-negative and set to zero relative telomerase activity.