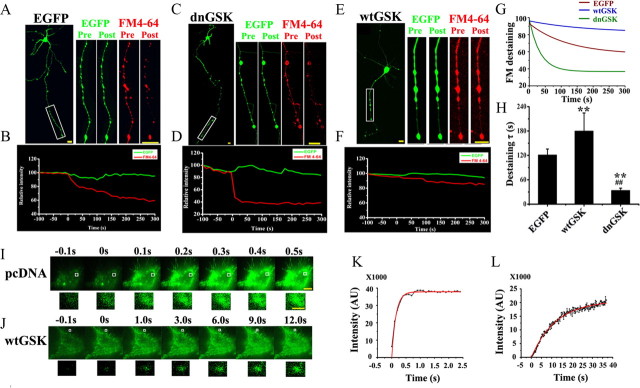
Figure 1.
A–H, GSK-3β inhibits presynaptic exocytosis. K+-evoked release of FM4-64 was recorded by confocal microscope. Dissociated hippocampal neurons transfected with EGFP-vector or EGFP-dnGSK-3β or EGFP-wtGSK-3β were measured by decline of FM4-64 for the vesicle release at the axon terminals (boxes). A, C, E, The images were captured before (Pre) and 5 min after (Post) K+ treatment. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, D, F, The kinetic curves were recorded from ∼100 s before to ∼5 min after K+ stimulation. G, H, Single-exponential decay functions were fitted to the diagrams with fluorescence intensity changes of FM4-64 analyzed by ImageJ software (G) and the time constant τ (H). I–L, Mean ± SD, ANOVA, Student's t test; **p < 0.01 versus EGFP; ##p < 0.01 versus wtGSK (n = 10∼12). I, J, K+-evoked release of pHluorin-Syb recorded by TIRFM: N2a cells were cotransfected with pHluorin-Syb and pcDNA3.0 (I) or wtGSK-3β (J) for 24 h. I, J, Consecutive images with enhanced fluorescence intensity after K+ stimulation were collected and amplified (from the boxes). Scale bar: 10 μm; 1 μm for amplification. K, L, The intensity of pHluorin was plotted and fitted to an exponential growth curve. The results show that overexpression of wtGSK-3β retards the K+-stimulated exocytosis.