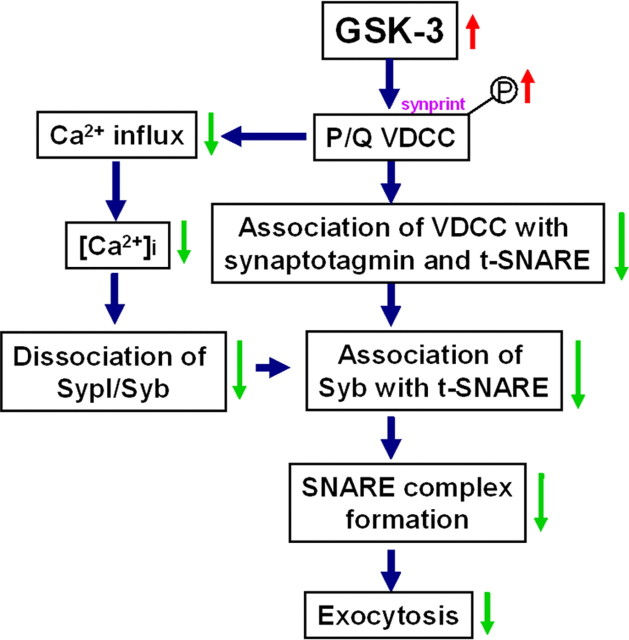
Figure 6.
A schematic diagram showing the mechanisms underlying the GSK-3-inhibited presynaptic exocytosis of vesicles. According to the results presented in the current study, we propose that activation of GSK-3β may inhibit the exocytosis by phosphorylating/inactivating P/Q-type VDCC and arresting Ca2+ influx, which disrupts the interaction of synaptic proteins, including decreasing the association of Syb with t-SNARE, decreasing the dissociation of Syb from SypI, and decreasing the association of LII-III with synaptotagmin and the t-SNARE (t-SNARE, syntaxin, and SNAP25).