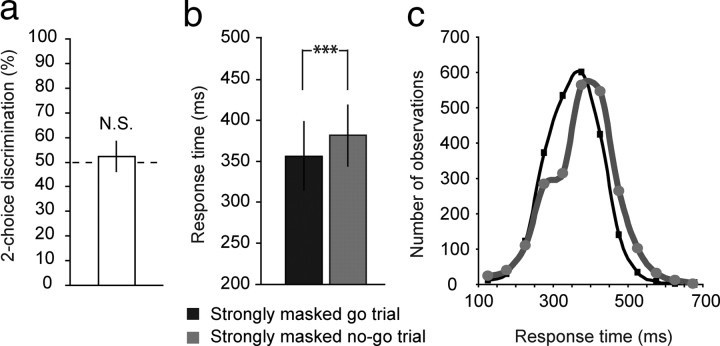
Figure 2.
Strongly masked (unconscious) no-go signals slow down responses. a, Participants were unable to discriminate between trials with a strongly masked square or diamond, as revealed by chance-level performance in a two-choice discrimination task administered after the main experiment. b, Although strongly masked no-go signals could not be perceived consciously, they still triggered inhibitory control processes, as revealed by significantly longer response times on these trials than on strongly masked go trials. c, Response time distributions of strongly masked no-go trials and strongly masked go trials. All plots indicate mean performance ± intersubject SDs.