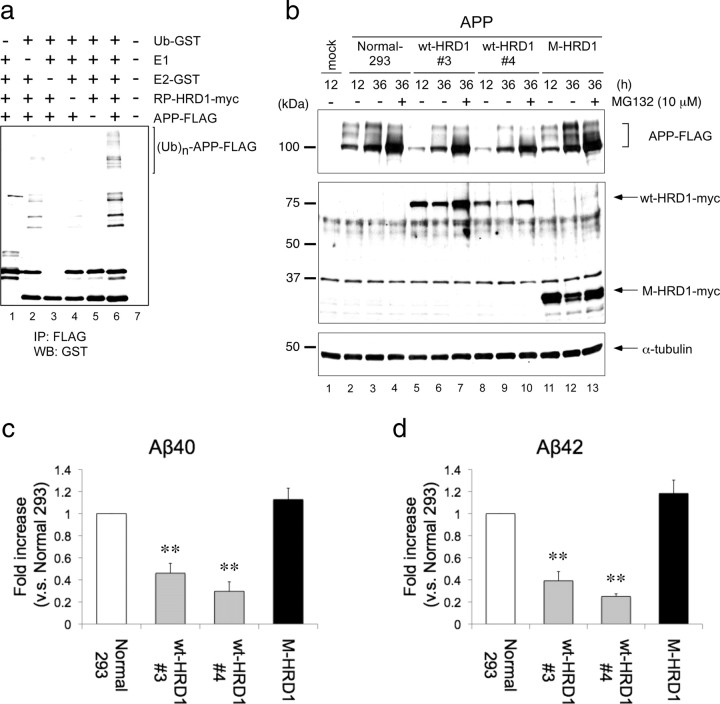
Figure 4.
Ubiquitination and degradation of APP by HRD1. a, In vitro ubiquitination assay. The reaction products, containing APP protein produced by a transcription/translation system, were mixed in the reaction buffer with E1 (rabbit), E2 (GST-UbcH5c), E3 (GST-RP-HRD1), and GST-ubiquitin. The reaction mixture was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-GST antibody. b, Degradation of APP by HRD1. Normal HEK293 cells and those stably expressing wt-HRD1, two stable cell lines (3 and 4), or M-HRD1 were transiently transfected with APP-FLAG and incubated for the indicated periods in the presence or absence of 10 μm MG132 for 12 h. The total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG (first panel), anti-myc (second panel), anti-α-tubulin (third panel) antibodies. c, d, Aβ levels were measured by a sandwich ELISA in b. HEK293 cells and those expressing wt- and M-HRD1 were transiently transfected with APP-FLAG. Data (pg/ml Aβ peptide) are normalized to the amount of APP mRNA quantified by real-time PCR. Results are expressed as a fold increase compared with normal cells (mean ± SEM; n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction (M-HRD1 vs wt-HRD1; **p < 0.01).