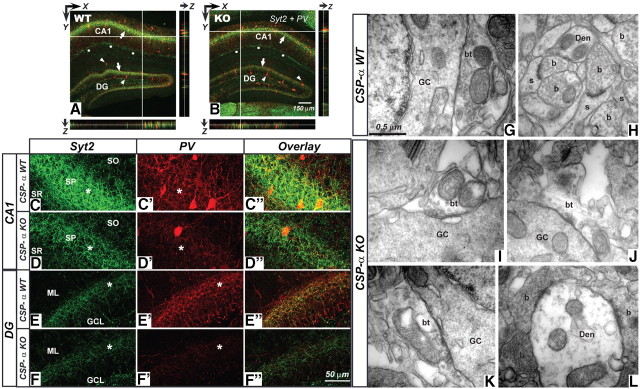
Figure 5.
Reduction in synaptic Syt2 and PV labeling and degeneration of basket cell terminals in CSP-α KO hippocampus. A, B, Confocal images from WT (A) and CSP-α KO (B) hippocampal slices labeled with anti-Syt2 (green) and anti-PV (red) antibodies. Stereological analysis shows no differences in the number of PV-positive somata (arrowheads) between the CSP-α WT and CSP-α KO hippocampus at P31–P40. However, note the different intensity in synaptic labeling (arrows) in the stratum pyramidale and granule cell layer. Syt2 staining also detected at the stratum lacunosum moleculare (dots). Labeling profiles through the z-axis demonstrate homogenous antibody penetration through the whole slice. C–D″, CA1 region in WT (C–C″) and KO (D–D″) hippocampal slices. Weaker Syt2 (green) and PV (red) labeling can be seen in the KO stratum pyramidale (asterisks). E–F″, Dentate gyrus in WT (E–E″) and KO (F–F″). There is a reduction in PV-positive puncta in the CSP-α KO (asterisks). Data from four WT and four KO littermates. G–L, EM analysis of excitatory (H, L) and inhibitory (G, I–K) synapses in the dentate gyrus. In the WT, GABAergic axon terminals (bt) (G) from basket cells establishing GABAergic synapses around the somata of granule cells (GC) are medium to large in size and are filled with synaptic vesicles. In the CSP-α KO mice (I–K), these terminals are smaller in size with less synaptic vesicles. In contrast, glutamatergic axon terminals (b) establishing excitatory synapses with dendritic shafts (Den) or spines (s) in the molecular layer of the dentate gyrus or close to the somatic inhibitory synapses are virtually similar in both WT (H) and CSP-α KO (L) mice. SO, Stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; ML, molecular layer; GCL, granule cell layer.