Figure 3.
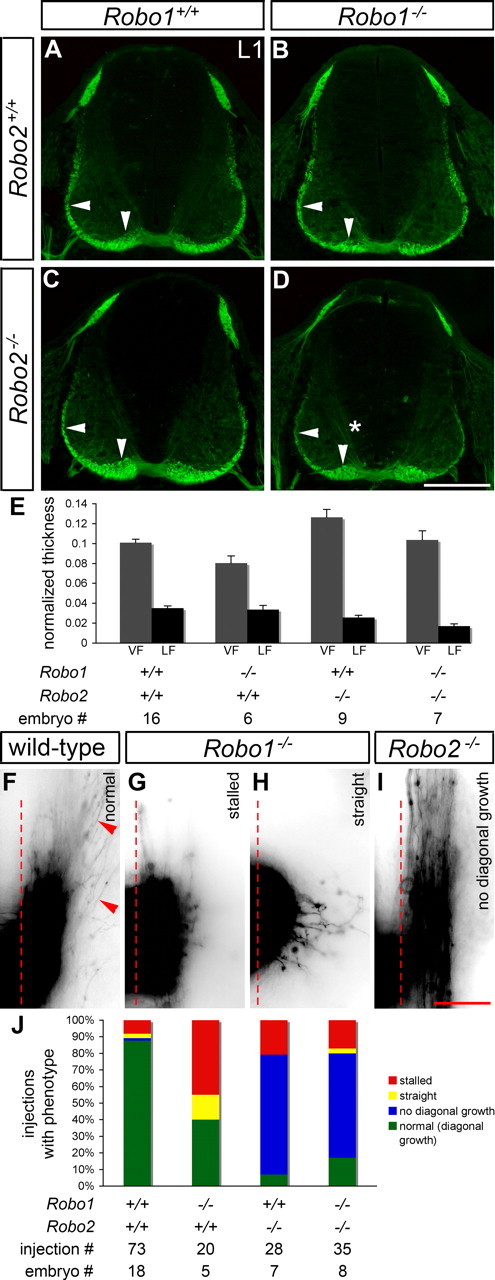
Sorting of post-crossing commissural axons into the ventral and lateral funiculi is abnormal in mice lacking Robo1, Robo2, or Robo1 and Robo2. A–E, Transverse sections of E11.5 spinal cords from mice with the indicated genotypes were stained for L1 to label post-crossing commissural axons, and the thickness of the VF and LF was quantified (see Materials and Methods). In Robo1 mutant embryos (B), the VF (vertical arrowhead) is thinner than in wild-type embryos (A) (p = 0.0322). In mice lacking Robo2 (C), the VF is thicker than in wild type (p = 0.0027), whereas the LF (horizontal arrowhead) is thinned (p = 0.006). Thinning of the LF is also observed in Robo1−/−; Robo2−/− embryos (D) (p < 0.0001), but the VF appears similar to wild type. L1 immunostaining is observed in association with pre-crossing segments of commissural axons (*) in embryos lacking Robo1 and Robo2 (D). Error bars in E indicate SEM. F–I, Open-book preparations of E11.5 wild-type, Robo1−/−, Robo2−/−, and Robo1−/−; Robo2−/− embryos were injected with DiI as described in Figure 1. The examples shown are inverted grayscale images. In wild-type embryos (F), commissural axons turn anteriorly (top) after crossing the contralateral border of the floor plate (dashed line). Many axons (arrowheads) project diagonally away from the floor plate, as they start growing dorsally while continuing anteriorly. In Robo1 mutant embryos (G, H), axons often stall just after leaving the floor plate (G) or fail to turn longitudinally and instead grow dorsally (H). In Robo2−/− (I) and Robo1−/−; Robo2−/− (data not shown) embryos, axons turn anteriorly after crossing but fail to grow dorsally. J, A quantification of the DiI analysis. Stalling, as shown in G, and straight growth after crossing (see H) are common in Robo1 mutants, whereas a failure to project diagonally (see I) is observed in the majority of injection sites for Robo2 and Robo1/2 mutants. Scale bars: A–D, 200 μm; F–I, 50 μm.
