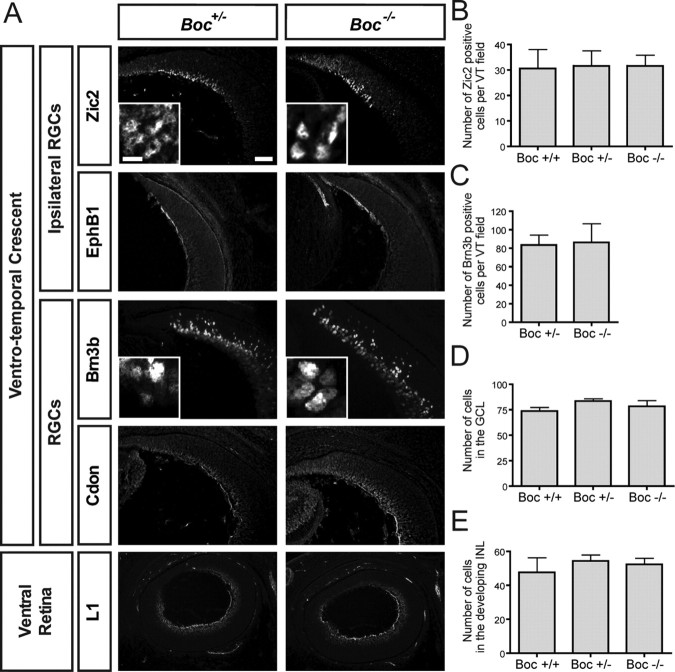
Figure 4.
Boc mutant mice have normal retinal cell fate. A, Horizontal sections of mouse E15 ventral retina from Boc +/− and Boc −/− mice were stained with various RGC markers. Zic2 is an ipsilateral RGC nuclear marker. EphB1 is an axonal marker of ipsilateral RGCs. Brn3b is a general RGC nuclear marker. Cdon labels RGCs and their axons. The lowest panels showcross-sections of the whole ventral retina (with the temporal side up) stained with L1, a marker of all RGC axons. None of these markers appears to be different in Boc −/− retina compared with Boc +/− retina. Insets represent a zoom in of the GCL. B, Quantification of the number of Zic2-positive RGCs shows that the number of ipsilateral RGCs is similar between Boc +/+, Boc +/−, and Boc −/− retinas. C, Quantification of the number of Brn3b-positive RGCs shows that the numbers of RGCs in the VT region are similar between Boc +/− and Boc −/− retinas. D, E, The number of cells in the VT region of the GCL (D) and the developing INL (E) is not significantly different between wild-type, Boc +/−, and Boc −/− retinas. n ≥ 3 embryos for each genotype. Scale bars, 50 μm; insets, 10 μm.