Figure 5.
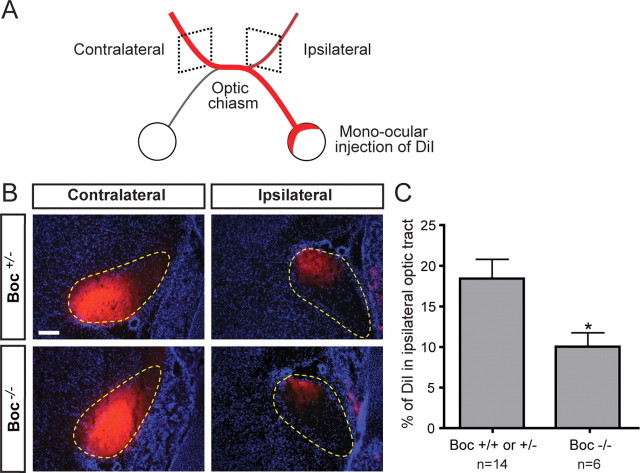
Normal segregation of ipsilateral axons at the optic chiasm requires Boc. A, Schematic of the rostral part of the E18.5 mouse visual system after mono-ocular injection of DiI crystals (red) in the whole retina. B, Coronal sections of E18.5 Boc +/− and Boc −/− optic tracts after mono-ocular injection of DiI crystals (red) and counterstaining with DAPI (blue). The optic tracts are circled with yellow dashed lines. The DiI intensity is lower in the ipsilateral tract of Boc −/− compared with Boc +/− mice. Note that although these images show saturated pixels for ease of viewing the faint ipsilateral signal, the quantification was performed on unsaturated images. C, Quantification of the percentage of DiI signal in the ipsilateral optic tract as a proportion of the total DiI signal from the contralateral and ipsilateral optic tract reveals a significant decrease in ipsilateral projections in Boc −/− mice compared with control (Boc +/− or Boc +/+) mice [18.5 ± 2.5% (n = 14 embryos) and 10.0 ± 1.8% (n = 6), respectively; p < 0.05 using Student's unpaired t test]. Scale bar, 100 μm.