Figure 5.
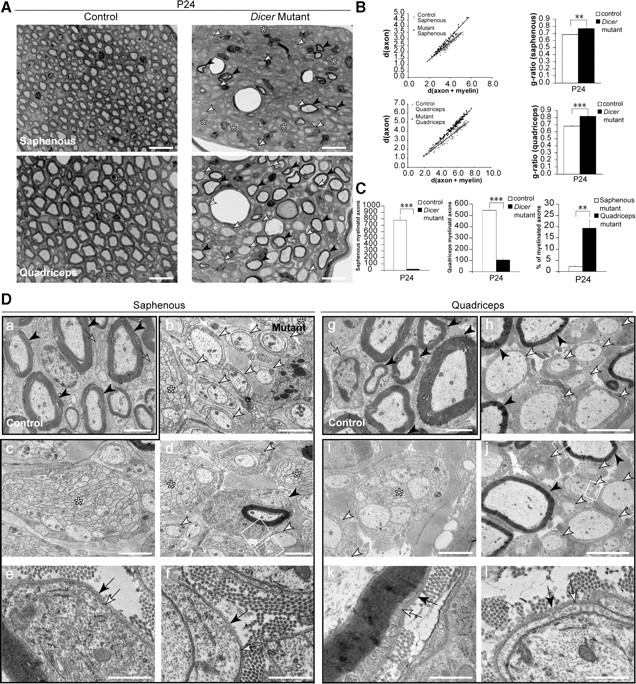
Sensory- and motor-enriched femoralis branches were distinctively affected on loss of Dicer in Schwann cells. A, Toluidine blue-stained sections (0.5 μm) of P24 saphenous nerve, exclusively composed of sensory axons, and quadriceps nerve, composed of 40–50% myelinated motor axons. Control nerves were widely myelinated, but mutant nerves displayed very few myelinated fibers (black arrowheads), several promyelinating profiles (white arrowheads), and some small axonal bundles (asterisks). Scale bars, 20 μm. B, Scatterplot graphics of measurements performed in control and mutant animals showed thinner myelin sheaths on fibers that were myelinated in mutant animals. Every mutant animal analyzed displayed a higher average g-ratio than control littermates (n = 3, p = 0.0014 for dorsal roots; n = 3, p < 0.0001 for ventral roots). C, The total number of myelinated fibers was quantified in the entire nerve cross section of control and mutant animals. Both saphenous (n = 3, p = 0.00011) and quadriceps (n = 3, p < 0.0001) nerves displayed a small fraction of myelinated fibers when compared with control counterparts. Surprisingly, when comparing myelinated fibers in the mutant saphenous nerves to the mutant quadriceps nerves, the saphenous nerve showed an approximately ninefold lower percentage of myelinated axons than the quadriceps (n = 3, p = 0.0077). Da–l, EM micrographs of saphenous (a–f) and quadriceps (g–l) nerves. Control nerves (a, g) displayed thoroughly myelinated fibers (black arrowheads) and mature nonmyelinating SCs (gray arrows). Mutant saphenous nerves displayed bundles of naked axons (b–d, asterisks), 1:1 not-myelinated profiles (b, d, white arrowheads), and very rare myelinated fibers (d, black arrowhead). Quadriceps nerves from Dicer mutants presented 1:1 not-myelinated profiles (h–j, white arrowheads), bundles of unsorted axons (i, j, asterisks), and some myelinating SCs (h, j, black arrowheads). The myelinating and promyelinating SCs presented a basal lamina (e, f, k, l, black arrow) tightly apposed to the SC abaxonal plasmalemma (e, f, k, l, white arrow). Both mutant nerves displayed very high levels of collagen when compared with controls. Scale bars: h, j, 5 μm; a–d, g, i, 2 μm; e, f, k, l, 0.5 μm. Error bars display ± SEM.
