Figure 3.
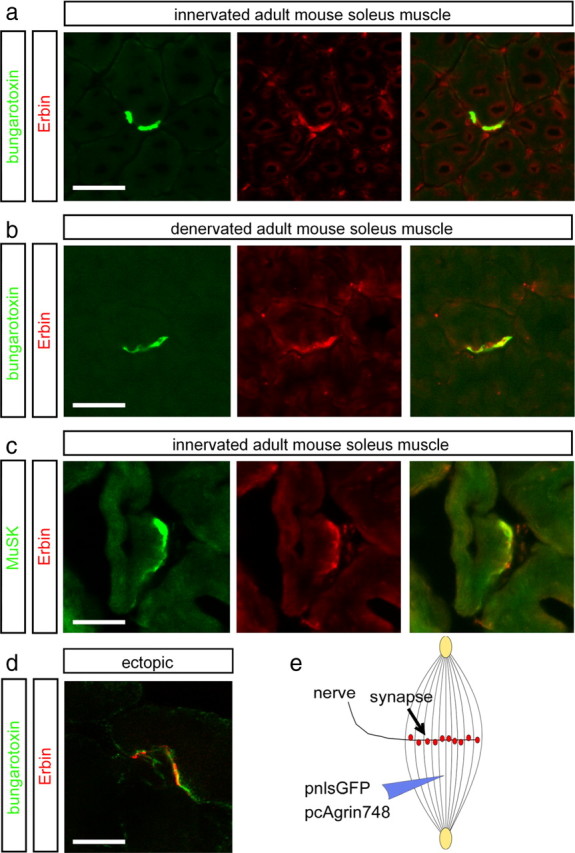
Erbin colocalizes with postsynaptic specializations in vivo. a, b, Frozen 12-μm-thick cryotome cross sections of surgically denervated (5 d after operation) or innervated (contralateral) mouse hindlimb muscles were immunoassayed with rhodamine-α-bungarotoxin (shown in red) and an Erbin-reactive antibody (shown in green). Note that the colocalization between Erbin and postsynaptic specializations is also present in the absence of the nerve. c, Direct colocalization between MuSK and Erbin was verified by staining muscle cross sections with MuSK- and Erbin-recognizing antibodies. d, To exclude a staining of terminal Schwann cells with Erbin-reactive antibodies, ectopic postsynaptic membranes were generated. A typical image showing subcellular colocalization of AChR clusters and Erbin at ectopic postsynaptic membranes is presented. e, As illustrated, nerve-derived agrin and a nuclear localized GFP (pnls-GFP) (Hashemolhosseini et al., 2000) were injected into single muscle fibers to generate ectopic postsynaptic membranes. d, Note that in d, a single projected image of a set of Z-images obtained by confocal microscopy is shown. Scale bar, 20 μm.
