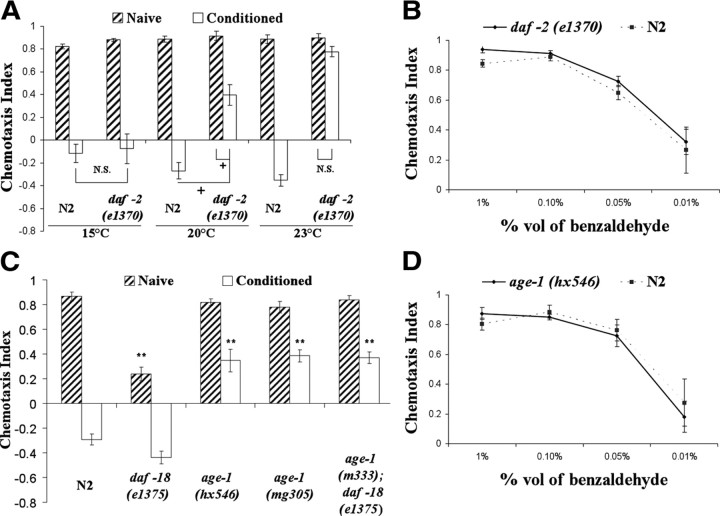
Figure 2.
Animals with mutations in the components of DAF-2 signaling are defective in benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity. For all panels in the figure, double asterisks represent significant differences from N2 within the same group (**p < 0.05 by Bonferroni's t test). Crosses represent significant differences between the indicated data points (+p < 0.05 by Bonferroni's t test). N.S., Not significant. Data represent means ± SEM. A, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants trained and tested at various temperatures. Wild-type N2 and daf-2(e1370) mutants were conditioned and tested to benzaldehyde at 15°C, 20°C, and 23°C. daf-2 mutants exhibited defective benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity when trained and tested at 23°C (the temperature at which daf-2 is presumably defective in function), but had normal benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity when trained at tested at 15°C (the permissive temperature). A three-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain, conditioning, and temperature F(2,71) = 23.564, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). B, Chemotaxis of N2 and daf-2(e1370) to various concentration of benzaldehyde at 23°C. N2 and daf-2(e1370) were comparable in their chemotaxis to 1, 0.1, 0.05, and 0.01% benzaldehyde, suggesting ins-1(nr2091) animals sense benzaldehyde normally at 23°C. A two-way ANOVA revealed a main effect of benzaldehyde concentrations, F(3,31) = 35.37, p < 0.05, and no main effect of strain F(1,31) = 1.682, p = 0.21 (n = 4 plates for each data point). C, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in mutants of the AGE-1 signaling pathway. age-1 mutants demonstrated partial associative plasticity defects. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain and conditioning, F(4,59) = 22.26, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). D, Chemotaxis of N2 and age-1(hx546) to various concentration of benzaldehyde. N2 and age-1(hx546) were comparable in their chemotaxis to various concentration of benzaldehyde, suggesting age-1(hx546) animals sense benzaldehyde normally. A two-way ANOVA revealed a main effect of benzaldehyde concentrations, F(3,31) = 27.42, p < 0.05, and no main effect of strain F(1,31) = 0.188, p = 0.66 (n = 4 plates for each data point).