Figure 4.
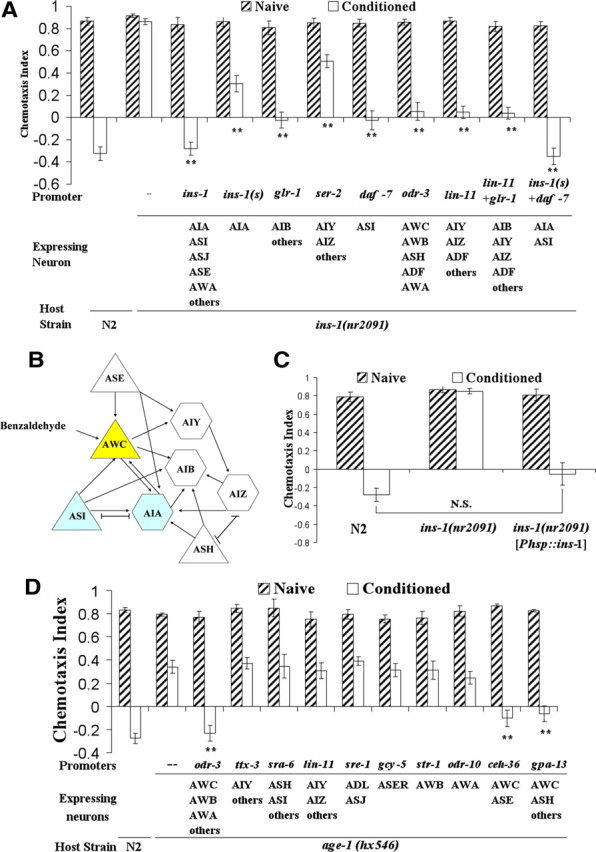
INS-1 can act from multiple neurons and AGE-1 acts in AWC to regulate benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity at the adult stage. For all panels in the figure, double asterisks represent significant differences from N2 within the same group (**p < 0.05 by Bonferroni's t test). N.S., Not significant. Data represent means ± SEM. A, Rescue effect of INS-1::VENUS expression under different promoters in ins-1 animals. Expression of INS-1::VENUS from multiple sets of neurons partially rescued the plasticity deficit in ins-1 mutants, and expression of INS-1::VENUS in ASI and AIA was sufficient to fully rescue the deficit. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain and conditioning, F(10,131) = 20.72, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). B, Part of the neural circuitry involved in benzaldehyde sensation (White et al., 1986). Arrows indicate synaptic connections; H shapes indicate gap junctions; triangles and hexagons represent sensory neurons and interneurons respectively. C, Rescue effect of ins-1 cDNA expression under a heat shock-inducible promoter in ins-1 animals. Animals were heat shocked at 33°C and allowed to recover before exposure to benzaldehyde in the absence of food. Expression of INS-1 under a heat shock promoter rescued the plasticity deficit in ins-1 mutants after heat shock. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain and conditioning, F(2,35) = 32.06, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). D, Rescue effect of AGE-1 expression using various promoters in age-1(hx546) animals. The learning defect is significantly rescued by the expression of AGE-1 in AWC neurons using the odr-3, ceh-36, and gpa-13 promoters. Expression of AGE-1 in AIY interneurons using ttx-3, in subsets of neurons including AIZ using lin-11 promoter, in ADL and ASJ neurons using the sre-1 promoter, in ASER neurons using the gcy-5 promoter, in AWB neurons using str-1 promoter, or in ASH and ASI neurons using promoter sra-6 did not rescue the plasticity defect in age-1(hx546) animals. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain and conditioning, F(11,143) = 12.18, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point).
