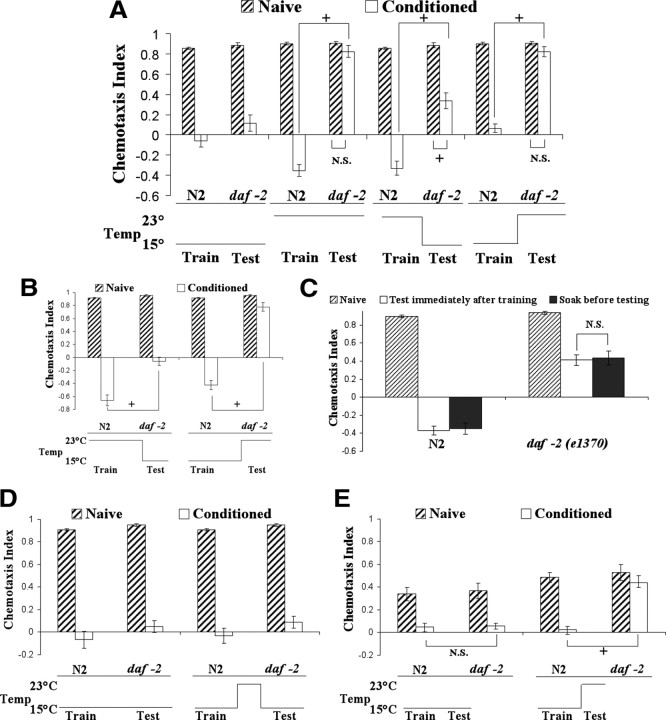
Figure 5.
DAF-2 signaling is partially involved in memory acquisition but essential in memory retrieval. For all panels in the figure, double asterisks represent significant differences from N2 within the same group (**p < 0.05 by Bonferroni's t test). Crosses represent significant differences between the indicated data points (+p < 0.05 by Bonferroni's t test). N.S., Not significant. Data represent means ± SEM. A, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants when DAF-2 signaling is disrupted during memory acquisition or retrieval. Wild-type N2 and daf-2(e1370) mutants were grown at 15°C and then conditioned at 15 or 23°C and tested to benzaldehyde at 15 or 23°C. Disruption of DAF-2 signaling during training partially blocked benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity while disruption of DAF-2 signaling during testing fully blocked this plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants. A three-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain, conditioning, and temperature F(3,127) = 13.30, p < 0.05 (n = 8 plates for each data point). B, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants when the conditioning period is extended to 2 h at two different temperatures. Disruption of DAF-2 signaling during training partially blocked benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity while disruption of DAF-2 signaling during testing fully blocked this plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants. A three-way ANOVA revealed significant interaction between strain, conditioning, and temperature F(1,47) = 77.63, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). C, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants given more time for functional DAF-2 restoration. Extending the restoration time of functional DAF-2 did not significantly change daf-2 mutants' conditioned response toward benzaldehyde. A two-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain and conditioning, F(2,35) = 33.54, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). D, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants with transiently disruption of DAF-2 signaling after conditioning. Animals were conditioned at 15°C, washed and left in 23°C M9 for 10 min before testing at 15°C. Transient disruption of DAF-2 signaling did not block benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants. A two-way ANOVA revealed no significant interaction between strain and conditioning F(2,35) = 33.54, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point). E, Benzaldehyde–starvation associative plasticity in daf-2(e1370) mutants when DAF-2 signaling is disrupted during memory retrieval. Animals were conditioned at 15°C and tested 15°C or 23°C for 10 min. daf-2 animals demonstrated a significant plasticity deficit when tested at 23°C for 10 min compared with that of wild-type N2. A three-way ANOVA revealed a significant interaction between strain, conditioning, and temperature F(1,47) = 7.08, p < 0.05 (n = 6 plates for each data point).