Figure 9.
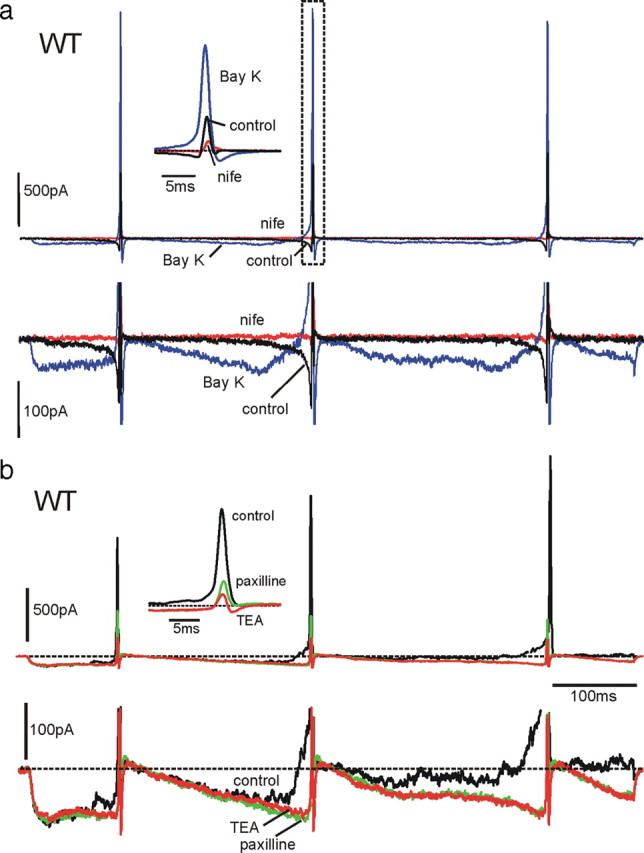
BayK-8644 and paxilline increase the net inward pacemaker current in WT-MCCs. a, In the top row are shown the effects of BayK-8644 (Bay K; 1 μm) and nifedipine (nife; 3 μm) on inward and outward currents during an action potential train clamp. As shown at more expanded vertical (bottom row) and timescales (inset), BayK-8644 increases dramatically the prespike current and generates a dominant BK current component during the three spikes. Both inward and outward currents are primarily blocked by nifedipine. Notice also the brief inward L-type current after the AHP associated with the closing of BayK-8644-modified LTCCs. This current contributed to the quick redepolarization after the increased AHP induced by BayK-8644. b, Effects of paxilline on K+ outward currents in a BayK-8644-treated WT-MCC. The DHP activator induces a large inward L-type current that activates a noisy BK outward current that rises gradually during the interpulse. Paxilline blocks the noisy current, increases the net inward prespike current, and drastically lowers the K+ outward component during the spike (inset). The residual K+ outward current is mainly associated with voltage-gated K+ channels. The block of the slow outward current by paxilline is similar to that induced by TEA, confirming that the current component blocked by paxilline is carried by Ca2+-activated BK channels.
