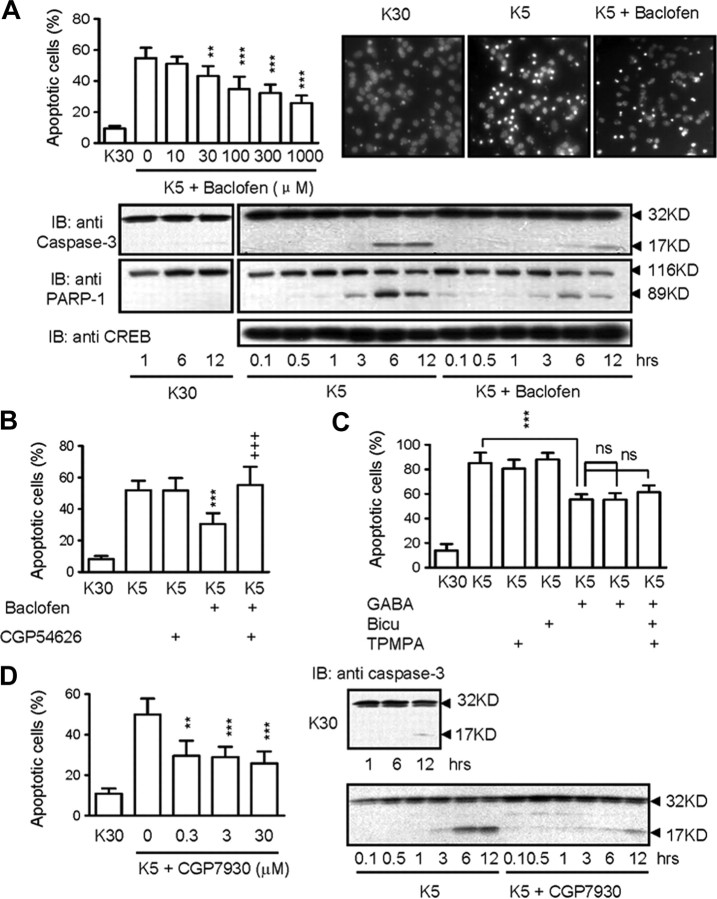
Figure 1.
GABAB receptor activation protect neurons from potassium-deprivation-induced apoptosis. A, Dose–response of baclofen on apoptosis when CGNs were transferred from high (30 mm K+, K30) to low (5 mm K+, K5) potassium concentrations for 24 h. Apoptotic cells were measured by TUNEL assay (left) and observed by Hoechst 33258 staining (right). Time course study of the effect of baclofen at 300 μm on caspase-3 activation and PARP activity were shown in the bottom panel and CREB protein expression was used as loading control. B, C, Effect of GABAA [bicuculline (10 μm)] and GABAC [TPMPA (10 μm)] receptor antagonists on apoptotic CGNs after GABA (100 μm) stimulation. For all TUNEL assay or Hoechst 33258 staining, cells were treated with drugs in K5 media for 18–20 h before fixing and staining. For caspase-3 activation, cells were treated with drugs in K5 media for 0.1–12 h. D, Dose–response of the GABAB receptor-positive allosteric modulator CGP7930 on apoptotic CGNs (left) and the effects of CGP7930 at 30 μm on caspase-3 activation (right). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, versus K30 conditions. +++p < 0.001; ns, no significance, versus in the absence of antagonist. The blots shown are representative of three separate experiments.