Figure 1.
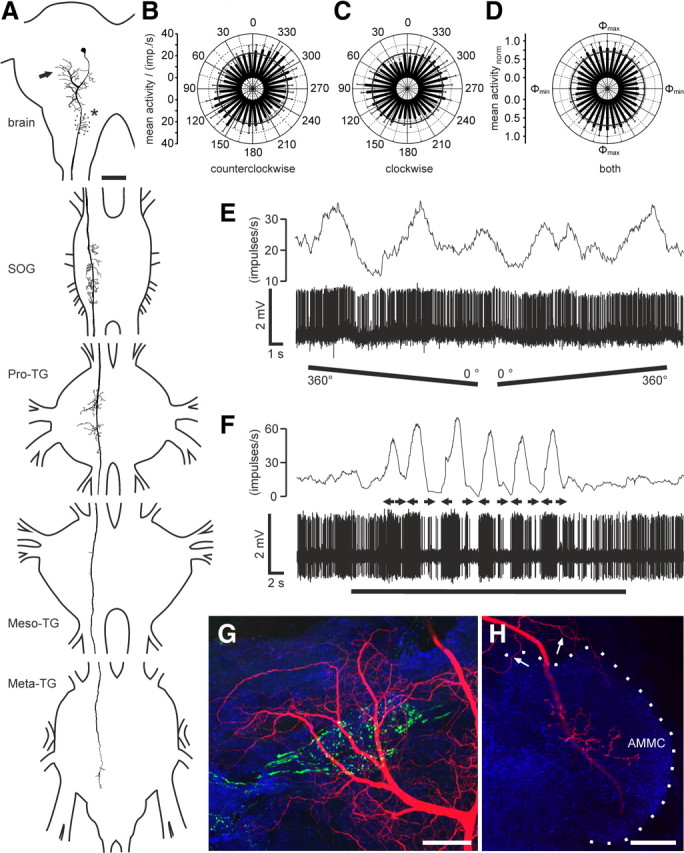
Morphology and response characteristics of ipsilaterally descending brain neurons. A, Reconstruction of arborizations in the brain (posterior view), SOG, and the three thoracic ganglia (dorsal view). Arborizations in all ganglia are confined to the ipsilateral hemispheres. Dendritic ramifications are in the posterior protocerebrum at the level of the posterior optic tubercle (arrow; POTu, gray shaded; see also G). The antennal mechanosensory and motor center (dotted line, asterisk; see also H) is invaded by beaded arborizations. An axonal fiber descends through the SOG with ramifications extending laterally and medially around the axon. In the Pro-TG, two characteristic areas of ramification extend laterally. The axon passes through the mesothoracic (Meso-TG) and metathoracic (Meta-TG) ganglion, with only sparse side branches, and could not be traced beyond the fused first abdominal ganglion. B, C, Circular diagrams of mean frequencies of action potentials plotted against E-vector orientation during dorsal stimulation with a rotating polarizer. Background activity is indicated by a black circle within each plot. B, During counterclockwise rotations of the polarizer, E-vector tuning (Φmax) was at 142° (n = 7; error bars indicate SD; bin size, 10°; p = 1.9 × 10−12). C, The preferred E-vector orientation during clockwise rotations (n = 7; error bars indicate SD; bin size, 10°; p = 2.2 × 10−8) had a Φmax of 111° and differed significantly from Φmax during counterclockwise rotations (n = 7; p = 0.009, Student's t test for paired probes). D, Circular diagram showing normalized mean activities from all recordings (n = 6) to dorsal stimulation through a rotating polarizer with Φmax set to 0°. Background activity is indicated by a black circle. E, Spike train (bottom trace) and mean spiking frequency (top trace; gliding average with bin size of 1 s) from the same neuron as in B and C during a counterclockwise (360–0°) and a clockwise (0–360°) rotation of the polarizer. F, Responses to a moving black and white grating presented in front of the animal. A small cardboard with black and white stripes was moved by hand from left to right and vice versa under unpolarized light condition (black bar). Black arrows indicate movement direction of the pattern as seen by the locust. The neuron with the soma in the left brain hemisphere was excited by movement from right to left and shows inhibition to moving bars from left to right. G, H, Morphological details in the brain. Maximum intensity views of optical sections (frontal plane; thickness, 2 μm) from confocal image stacks showing anti-synapsin staining (blue), anti-PDH immunostaining (green), and ramifications of the Neurobiotin-stained neuron (red). G, Maximum intensity projection of 78 optical sections showing ramifications around the posterior optic tubercle (POTu), which is marked with the anti-PDH antiserum. H, Maximum intensity projection of two combined stacks (76 optical sections), showing varicose arborizations in the antennal mechanosensory and motor center (AMMC). Some dendritic arborizations are visible dorsally from the antennal mechanosensory and motor center. Scale bars: A, 200 μm; G, H, 40 μm.
