Figure 4.
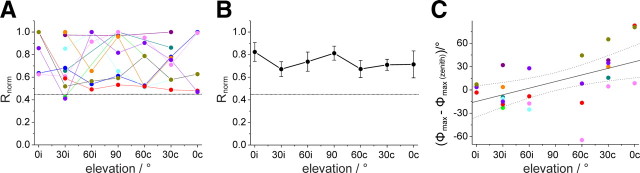
Polarized-light sensitivity and E-vector tuning of the descending SOG neurons when stimulated with polarized light from different elevations along the right–left meridian. A, Response amplitudes from individual recordings, distinguished by different colors, plotted against elevation of polarized-light stimulus. Elevation is plotted with respect to the location of the soma (0i–60i in the ipsilateral and 0c–60c in the contralateral hemisphere of the SOG) and was sampled along the right–left meridian with respect to the locust. Values were normalized to the largest R value of each neuron (i.e., the receptive field center). Data points are connected by lines for better visibility. Dotted line indicates background variability for the neuron type, which has been renormalized with respect to the mean receptive field center. B, Average receptive field for the examined SOG neurons. Dotted line, Background variability. Values are means ± SE. C, Deviations of Φmax values at different elevations from zenithal Φmax values. Differences in Φmax values are plotted against the elevation. A significant correlation was observed (Rcor = 0.53, p = 0.00453). Colors of data points correspond to the colors in A.