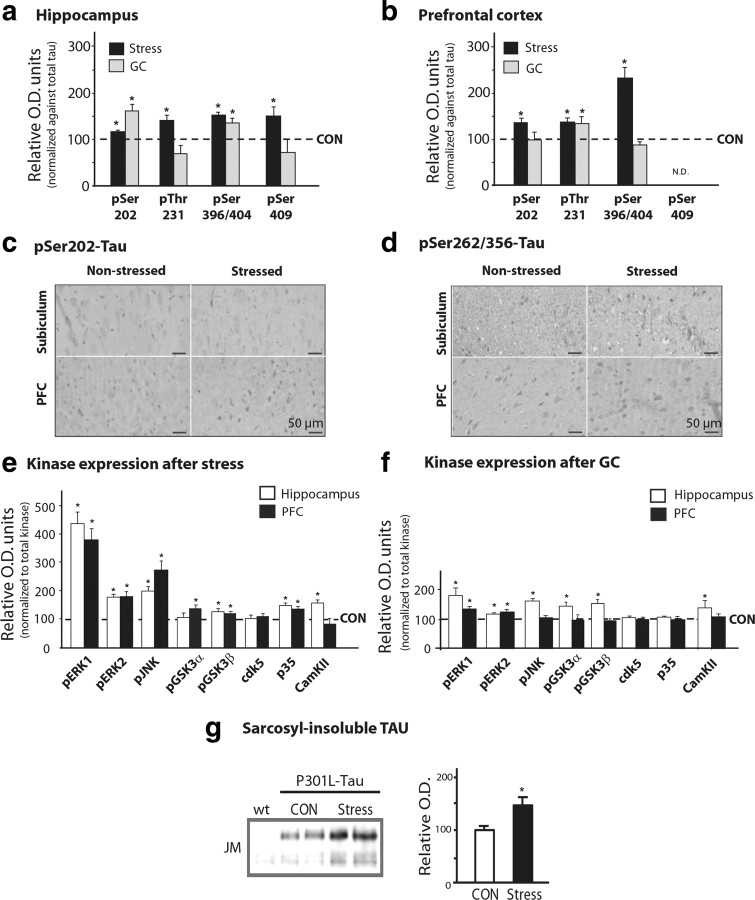
Figure 2.
Stress and GCs induce TAU hyperphosphorylation in the hippocampus and PFC. TAU phosphorylation profiles in the hippocampus and PFC of chronically stressed or GC-treated rats were monitored by Western immunoblotting and immunocytochemistry. a, b, Western blot analysis of TAU phosphorylation at different epitopes in hippocampus and PFC. TAU phosphorylation levels were normalized against total TAU levels (recognized by TAU-5); control (CON) animals are shown as dotted lines (100%). c, d, Immunohistochemical staining of pSer202-TAU and pSer262/356-TAU, in the hippocampus (subiculum) and PFC, using antibodies CP-13 and 12E8 antibodies, respectively. Immunoreactive signals were confined to the cell bodies of pyramidal neurons. e, f, Both stress and GCs increased the expression of a number of kinases in the hippocampus and PFC of animals exposed to stress or GC, compared with controls. For all phosphorylated forms of kinases, data were normalized with respect to total levels of the respective kinase. g, Western blot analysis of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions from P301L-TAU animals showing that chronic stress increases the levels of sarcosyl-insoluble TAU. All numerical data shown represent mean ± SEM values (N = 7), depicted with respect to data obtained in control tissues. *Significant differences from CON values (p ≤ 0.05).