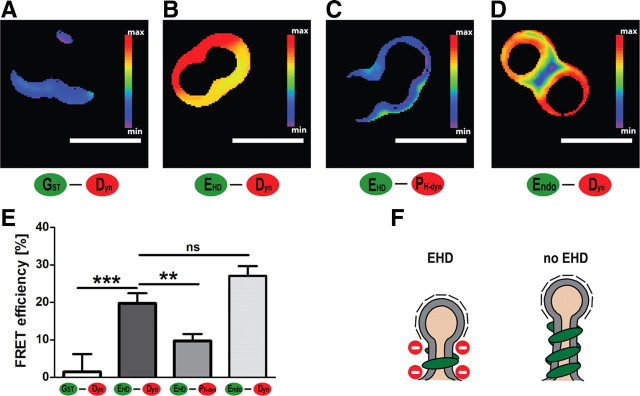
Figure 7.
Association between EHD and dynamin at membranes studied with FRET. A–D, FRET efficiency between different Alexa-labeled proteins measured on the surface of SUPER templates. A, Alexa 488-labeled GST and Alexa 546-labeled full-length dynamin. B, Alexa 488-labeled l-EHD and Alexa 546-labeled full-length dynamin. C, Alexa 488-labeled l-EHD and Alexa 546-labeled pleckstrin-homology (PH) domain of dynamin. D, Alexa 488-labeled full-length endophilin and Alexa 546-labeled full-length dynamin. E, Quantification of three independent FRET experiments for each combination of proteins (mean ± SEM, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.005). F, EHD appears to counteract excessive assembly of dynamin helices. Such an effect may be expected to promote vesicle budding as recent studies of dynamin function indicate that short helices promote membrane fission more effectively than long helices.