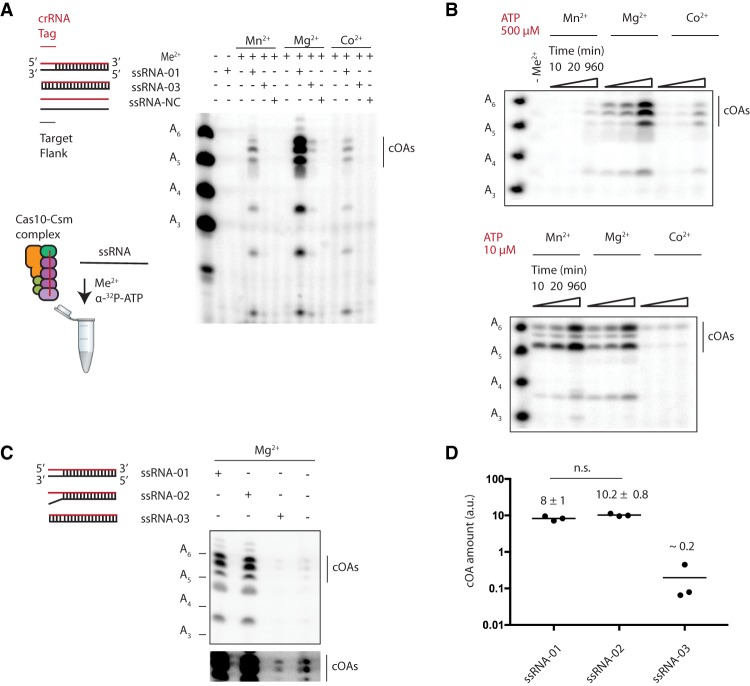
FIGURE 3.
Divalent metal and target RNA requirements for oligoadenylates synthesis by Cas10-Csm. (A) A schematic showing the components of the target RNA-dependent cOA synthesis reaction. The Cas10-Csm complex with a crRNA (red) is incubated with either a single-stranded 5′ tag mismatch RNA (ssRNA-01), a 5′ tag complementary RNA (ssRNA-03), or a noncomplementary RNA (ssRNA-NC). α-32P-ATP is added to reactions analyzed by electrophoresis. Migration of the cOA species by PAGE is compared to a ruler of linear oligoadenylate species (A3–A6). (B) A time-resolved analysis of cOA synthesis with three different divalent metals reveals that Mg2+ supports efficient cOA production when ATP is abundant, while both Mn2+ and Mg2+ can efficiently produce cOA under low ATP conditions. (C) The ssRNA-01 target RNA contains three positions in the 5′ tag–3′ flank region capable of base-pairing, whereas ssRNA-02 contains no 5′ tag–3′ flank base pairs. The quantity of oligoadenylates produced by these target RNAs was compared to a crRNA-target RNA with complete complementarity in the 5′ tag–3′ flank region (ssRNA-03). Standard and overexposed (lower) images of a representative gel containing the oligoadenylates are shown. (D) Three replicate reactions described in C were analyzed by PAGE, and oligoadenylates were quantified by densitometry to produce the means and standard deviations given in arbitrary units (a.u.). The difference between the ssRNA-01 and ssRNA-02 reactions is not significant (n.s., P < 0.05).