FIGURE 5.
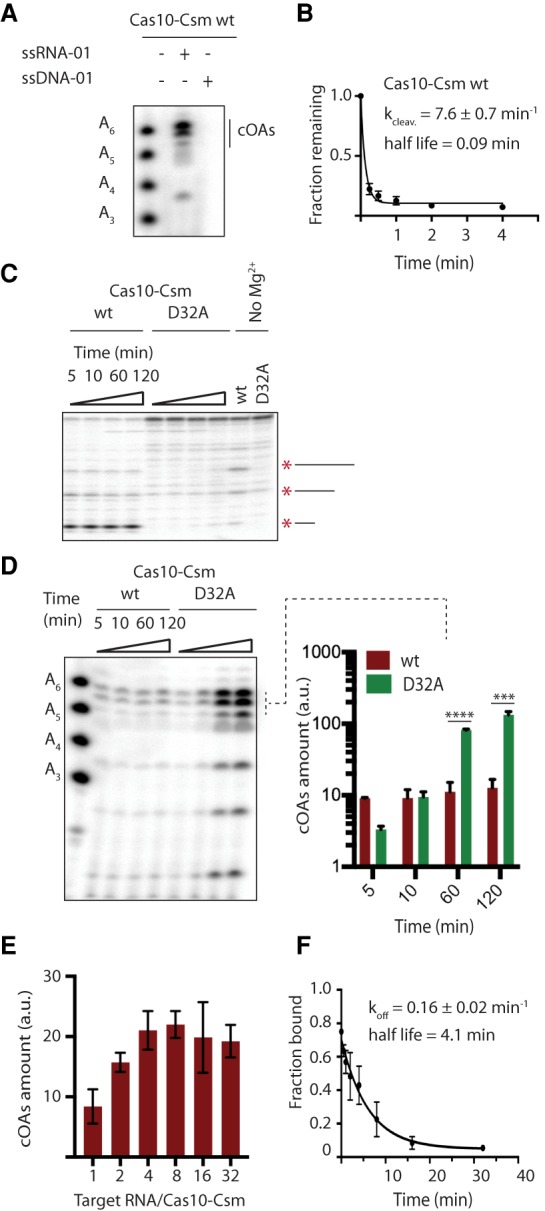
Cas10-Csm rapidly cleaves but slowly turns over target RNA. (A) PAGE analysis of a cOA synthesis reaction shows that a single-stranded DNA oligonucleotide complementary to spc1 crRNA is unable to activate cOA synthesis. (B) Three replicate reactions of target RNA cleavage (ssRNA-01) by wt Cas10-Csm were analyzed by PAGE to determine a rate constant for the process. (C) Cas10-Csm containing the Csm3 D32A mutant is unable to cleave target RNA, as shown by PAGE analysis of a reaction containing 32P-labeled ssRNA-01. An asterisk and line mark the location of RNA cleavage products. A control experiment incubating Cas10-Csm with ssRNA-01 for 120 min without Mg2+ is shown. (D) A time course of cOA synthesis analyzed by PAGE comparing the amount of cOA produced by wt and Cas10-CsmCsm3D32A. The reactions were performed in triplicate (one representative gel is shown), and a quantification of band intensities for three cOA species is shown. (***) P < 0.001; (****) P < 0.0001. (E) The amount cOA produced after 60 min was quantified for titrations of target RNA from a 1:1 mole ratio with Cas10-Csm up to a 32:1 mole ratio. (F) Dissociation of cleaved target RNA from its complex with crRNA bound Cas10-Csm was measured by a double filter binding assay to derive koff. Best-fit values for kcleav and koff are given along with standard error.
