FIGURE 1.
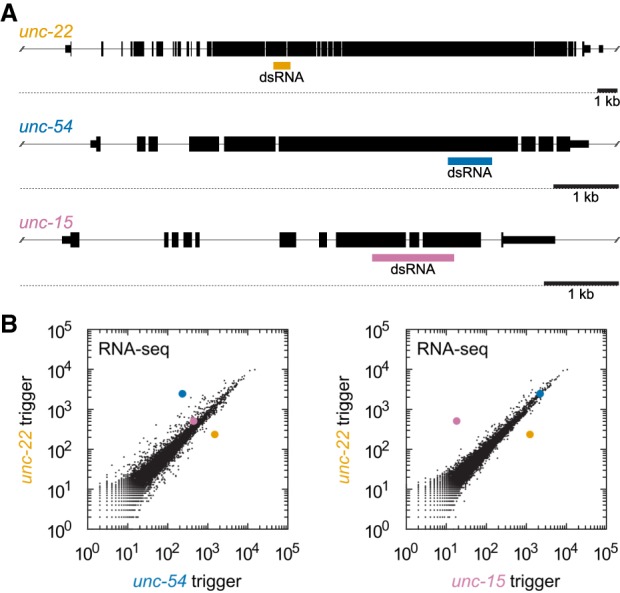
RNAi specifically knocks down transcripts targeted by double-stranded RNA triggers. (A) Diagram of endogenous genes selected as exogenous RNAi targets. Large boxes represent coding regions; narrower boxes represent noncoding regions. Gene diagrams are to scale, with 1 kb scale bar shown. Colored boxes indicate double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) regions expressed in E. coli and fed to the animals to trigger RNAi. (B) Genome-wide RNA-seq of animals after RNAi against unc-22 (y-axis), unc-54 (x-axis, left plot), or unc-15 (x-axis, right plot). Genes are highlighted using the same color scheme as part A. Animals were synchronized and placed on feeding RNAi plates and allowed to develop until the ∼L4 larval stage (∼72 h). Similar knockdown was observed at other developmental stages (Supplemental Fig. S1). Off-diagonal genes other than unc-22, unc-54, and unc-15 are mostly collagens and other periodically expressed transcripts (Supplemental Fig. S2; Hendriks et al. 2014).
