Figure 21.
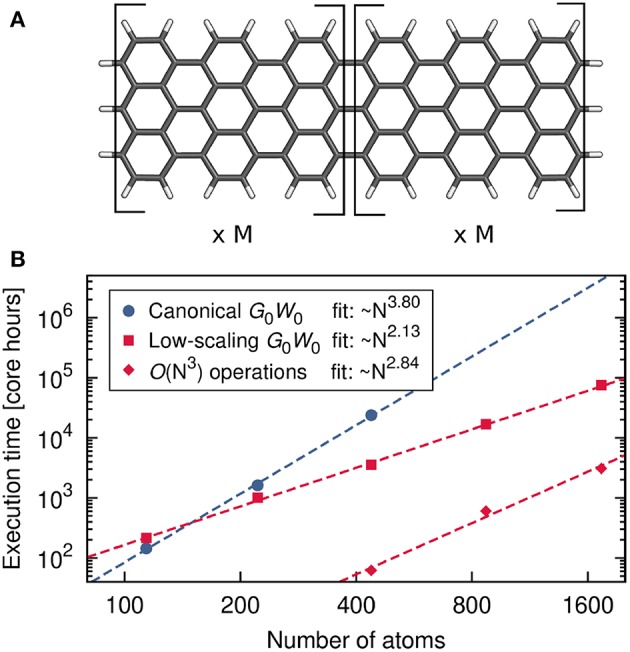
Scaling of state-of-the-art G0W0 implementations with respect to system size using graphene nanoribbons as a benchmark system. (A) Smallest graphene nanoribbon unit with 114 atoms. (B) Comparison of the scaling of the canonical G0W0 (Wilhelm et al., 2016) and the low-scaling implementation (Wilhelm et al., 2018). The latter requires operations of at most complexity (red diamonds). Dashed lines represent least-square fits of exponent and prefactor. Data retrieved from Wilhelm et al. (2018). Both algorithms are implemented in the CP2K program package.
