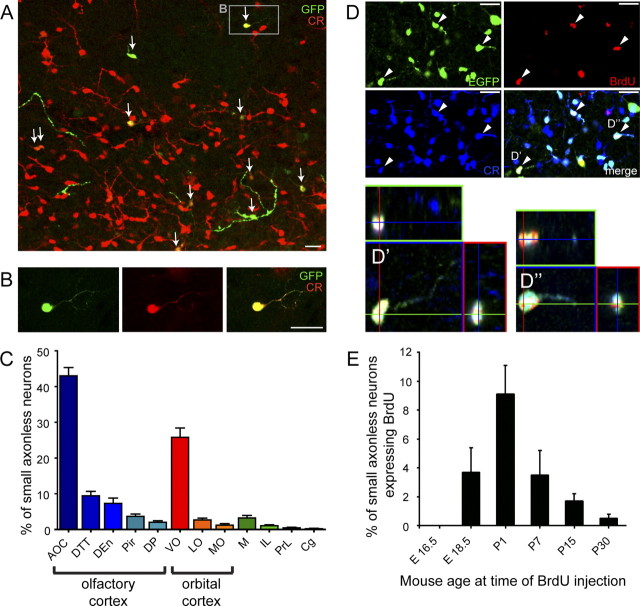
Figure 7.
Cortical distribution and time course of generation of small axonless neurons. A lentivirus expressing GFP was injected into the SVZ of P4 mice. After 3 weeks the distribution of GFP-positive cells in the brain was assessed. A, Calretinin expression (in red) in lentivirus-infected cells (GFP immunostaining in green) in the orbital cortex. Note the high number of calretinin-expressing small axonless neurons in this area. B, Example of virus-infected small axonless neurons (enlargement of the area indicated in A) showing calretinin expression. C, Differential distribution of small axonless neurons in the indicated cortical regions. The majority of small axonless neurons reside in olfactory (AOC, DTT, DEn, Pir, DP) and orbital (VO, LO, MO) cortices, 65% and 30%, respectively. D, E, BrdU was injected in 5HT3-EGFP mice to study the developmental regulation of small axonless neuron generation. D, EGFP/CR double-positive cortical cells in a 5HT3-EGFP mouse injected with BrdU at P1 coexpress BrdU (arrowheads), indicating that they were generated at P1. D′, D″, Magnifications of EGFP/CR/BrdU triple-positive cells. E, Bar histogram showing the percentage of BrdU+ small axonless neurons following BrdU injections at the indicated mouse age. Scale bars, 20 μm. AOC, Anterior olfactory cortex; DTT, dorsal tenia tecta; Den, dorsal endopiriform nucleus; Pir, piriform cortex; DP, dorsal peduncular cortex; VO, ventral orbital cortex; LO, lateral orbital cortex; MO, medial orbital cortex; M, motor cortex; IL, infralimbic cortex; PrL, prelimbic cortex; Cg, cingulate cortex.