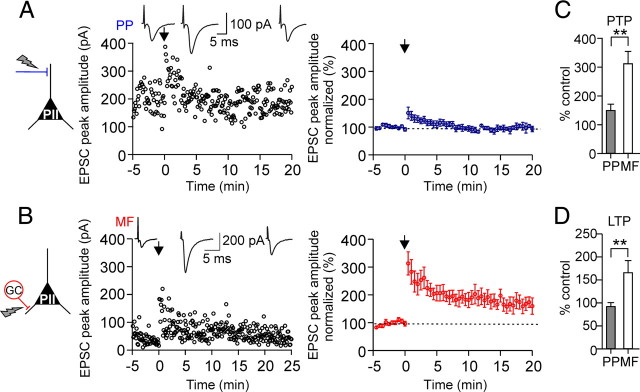
Figure 3.
Afferent-specific expression of LTP in perisomatic inhibitory interneurons. A, A nonassociative BFS applied to PP–PII synapses in combination with brief suprathreshold depolarizations in the postsynaptic cell (see Materials and Methods) induces PTP but not LTP. Left, Individual EPSC peak amplitudes from a single experiment are plotted against time before and after pairing. The nonassociative BFS was applied at t = 0 ms (arrow). Insets on top, Average EPSCs (30 traces) during the baseline period (left), during PTP (middle), and 15–20 min after the induction protocol (right). Right, Summary time course of EPSC peak amplitudes evoked at PP–PII synapses (blue) before and after pairing from eight cells. EPSCs were averaged over 30 s intervals and normalized to baseline values. B, Corresponding data for MF–PII synapses. At the MF input, pairing resulted in a PTP followed by a marked LTP (10 cells). C, D, Summary bar graphs comparing the effect of the applied nonassociative BFS on the peak amplitude of average EPSCs during the PTP (C) and the LTP phase (D) evoked by extracellular stimulation of the PP or the MF inputs. **p < 0.01; two-tailed Student's t test and Mann–Whitney U test. Average measurements are represented as mean ± SEM.