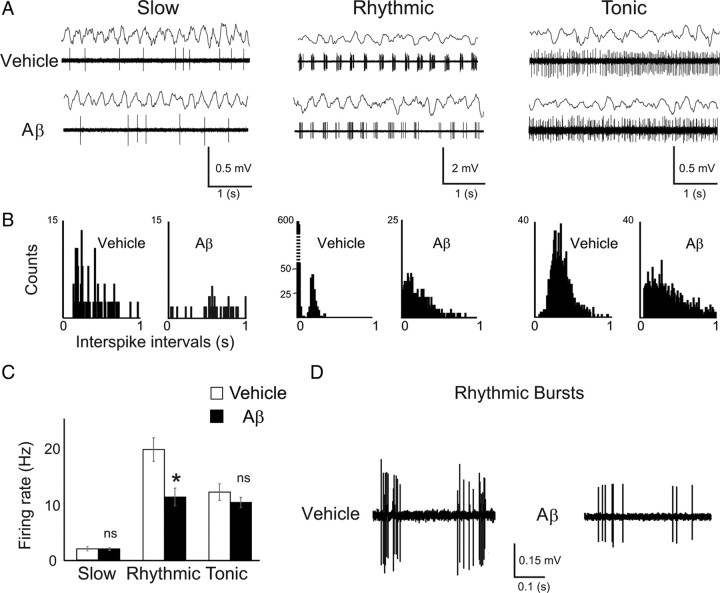
Figure 3.
Decreased rhythmic bursting activity in medial septal neurons after hippocampal Aβ injection. A, Examples of medial septal neurons electrophysiologically classified as slow, rhythmic, or tonic for vehicle- and Aβ-treated animals during hippocampal θ epochs (top traces). B, Corresponding interspike interval histograms for each class of cells in vehicle-treated (left-hand graph for each cell type) and Aβ-treated animals (right-hand graph for each cell type). C, Mean spontaneous firing rate for each class of medial septal neurons from vehicle-treated (white bars, n = 49) and Aβ-treated animals (black bars, n = 53); *p < 0.05, ANOVA with group and cell class as factors. D, Examples of rhythmic bursts in rhythmic neurons from vehicle-treated (left) and Aβ-treated animals (right). The rhythmic bursting activity in medial septal neurons is specifically altered in Aβ-treated rats.