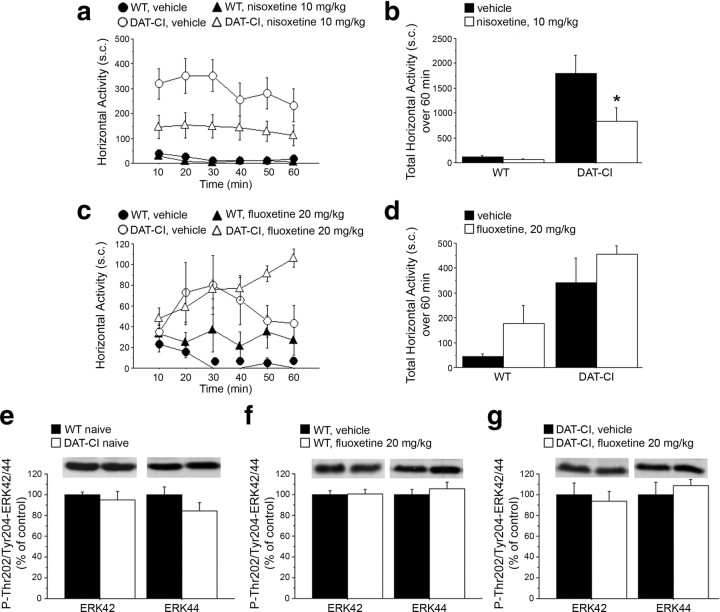
Figure 3.
Effect of selective NET and SERT inhibitors on DAT-CI motor activity. Horizontal motor activity induced in WT and DAT-CI mice by intraperitoneal injection of 10 mg/kg nisoxetine (WT, n = 7; DAT-CI, n = 11) or vehicle (WT, n = 7; DAT-CI, n = 8) (a, b) or subcutaneous administration of 20 mg/kg fluoxetine (n = 7 per genotype) or vehicle (n = 4 per genotype) (c, d), after 1 h of cage habituation. Locomotion is expressed as number of sector crossings, measured every 10 min over a 1 h test, and presented as time course (a, c) or total activity (b, d). P-Thr202/Tyr204-ERK42/44 protein levels were determined by Western blotting in the striatum of WT (n = 8) and DAT-CI (n = 7) naive mice (e), 20 mg/kg fluoxetine- or vehicle-injected WT (n = 6 per treatment) (f) and DAT-CI (g) mice (20 mg/kg fluoxetine: n = 5; vehicle: n = 6). The top panels show representative blots comparing the different genotypes or treatments, for each protein detected. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus vehicle group within genotype (one-way ANOVA). Genotypes and treatments are as indicated.