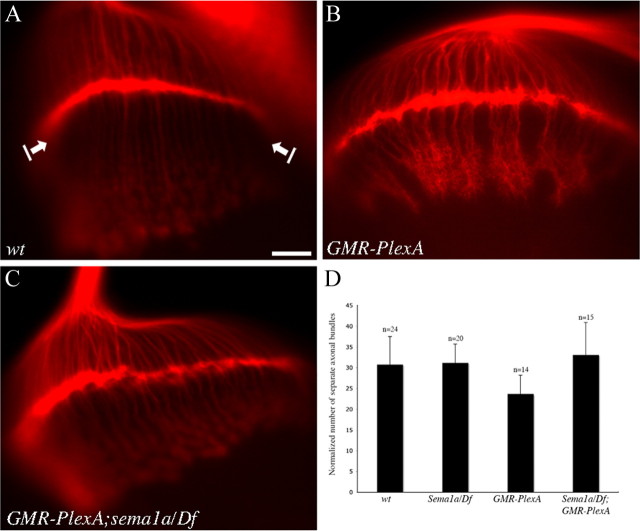
Figure 6.
PlexA functions upstream of sema1a. A, Wild type. B, Overexpression of PlexA under control of GMR-GAL4-induced R-cell axonal hyperfasciculation. C, The PlexA-induced hyperfasciculation phenotype was suppressed when sema1a was disrupted. D, The number of separate axonal bundles that are located between lamina and medulla was counted. The data were normalized with the row number of R-cell clusters in the eye disc. Compared with wild type, overexpression of PlexA induced the formation of thicker bundles and thus significantly decreased the number of separate R-cell axonal bundles (p = 0.0012). Compared with that of PlexA overexpression in wild-type background, the number of separate axonal bundles in PlexA-overexpression mutants in which the sema1a gene was disrupted, was increased significantly (p = 0.0005). Error bars denote SE. Scale bar, 20 μm.